Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090428-15
- Publication
- Behra et al., 2009 - Phoenix is required for mechanosensory hair cell regeneration in the zebrafish lateral line
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
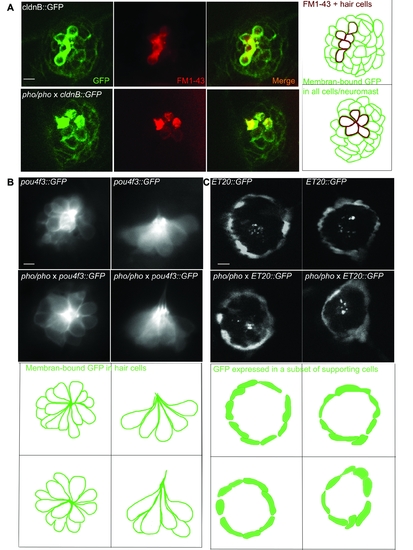
Live imaging of transgenic lines crossed into the phoenix background show no differences from wild-type larvae. A. We crossed the phoenix mutant line into the cldnB::GFP transgenic background, which expressed GFP (green in first and third panels) in all cells of the neuromast. We stained untreated 5 dpf larvae with FM1-43 (red in second and third a panel). Shown are images of live wild-type (top panels) and phoenix (bottom panels) neuromasts. A camera lucida drawing of each merged picture is highlighting the GFP positive cells contours (green) and the FM1-43 positive cells (red) in the fourth panel. B. We crossed the phoenix mutant line into the pou4f3::GFP transgenic background, which expressed GFP in all of the neuromast's hair cells. Dorsal views (left panels) and lateral views (right panels) of wild-type (top panels) and pho/pho (bottom panels) are shown. A camera lucida drawing of each panel is outlining the GFP positive hair cells of each respective 41 panel. C. We crossed the phoenix mutant into the ET20::GFP transgenic background, which expressed GFP in a subset of supporting cells known as the mantle cells. Two representative examples of wild-type (top panels) and of phoenix mutant (bottom panels) neuromasts are shown. A camera lucida drawing of each panel is outlining the GFP + cells of each respective panel. - 10 microns in all panels. |