Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090113-85
- Publication
- Snow et al., 2009 - Dynamic formation of microenvironments at the myotendinous junction correlates with muscle fiber morphogenesis in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
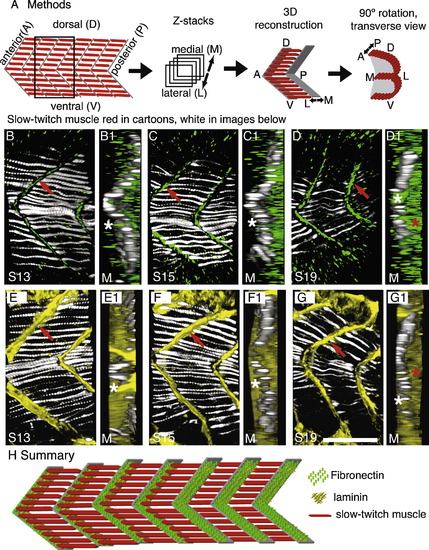
The ECM composition of the myoseptal tendon changes during early muscle development. See also Supplemental movies 1 and 2. Laminin persists, whereas Fn is down-regulated, resulting in Fn only concentrating adjacent to slow fibers. All panels were obtained on a Zeiss ApoTome. All Z-series are taken from the transition region of the embryo in which slow-twitch muscle is proceeding laterally. F59, which denotes slow-twitch muscle, is in white. (A) Cartoon summarizing methods. Embryos were stained for slow-twitch muscle (red in cartoons, white in data panels B?G) and Fn (green) or laminin (yellow). Z-series were taken and 3-dimensionaly reconstructed. Transverse views were obtained by rotating the 3-dimensional projection 90 degrees. (B?G) Projections of 20 somite-stage embryos (somite number indicated by S#) stained with F59 to visualize slow muscle (white), Fn (green, the Fn antibody recognizes Fn1 and Fn3 in zebrafish), or laminin (yellow). Lettered panels are side views, anterior left, dorsal top, red arrows denote staining at the myoseptal tendon. Panels numbered 1 are transverse views of the corresponding lettered panel. (D and G) Both Fn and laminin are observed in newly formed somites prior to slow muscle migration. Transverse reconstructions show that Fn and laminin are concentrated both medially (D1, G1, white stars, medial (M) is to the left) and laterally (red stars, lateral is to the right). (C and F) In slightly older somites, Fn is down-regulated medial to migrating slow muscle (C1, medial left, white star medial to the slow fibers shows very little Fn medially). Laminin distribution, however, does not change (F1, white star, laminin is robustly concentrated medially). (B and E) In myotomes, where slow muscle migration is complete, Fn is concentrated adjacent to slow fibers but not fast fibers (B1, white star). Laminin, however, is observed throughout the medial-lateral extent of the myoseptal tendon (E1, white star). (H) Cartoon summarizing dynamic changes in the myoseptal tendon. Slow-twitch fibers (red) are medial in younger somites (posterior, to the right), and laminin (yellow) and Fn (green) are located throughout the medial-lateral extent of the nascent myoseptal tendon. As slow-twitch muscle migrates laterally (in older anterior somites, to the left) Fn is down-regulated at the nascent myoseptal tendon medial to migrating slow-twitch fibers. Scale bar: 50 μm. |
| Antibodies: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | 20-25 somites |
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 9(1), Snow, C.J., and Henry, C.A., Dynamic formation of microenvironments at the myotendinous junction correlates with muscle fiber morphogenesis in zebrafish, 37-42, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns