Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-081222-25
- Publication
- Waxman et al., 2008 - Hoxb5b acts downstream of retinoic Acid signaling in the forelimb field to restrict heart field potential in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
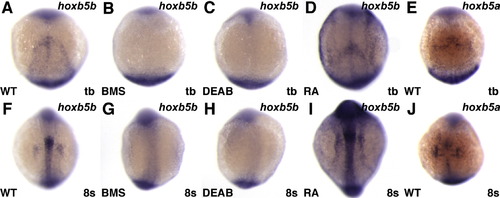
RA Signaling Positively Regulates hoxb5b Expression in the LPM Expression of hoxb5b at the tailbud (tb) or 8 somite stages, dorsal views, anterior to the top. (A?D and F?I) Reduction of RA signaling inhibits hoxb5b expression, and treatment with RA induces ectopic hoxb5b expression. (E and J) Expression of the hoxb5b paralog hoxb5a. Identification of hoxb5b as a RA-responsive gene is not surprising, since the chick and mouse Hoxb5 orthologs and the zebrafish paralog hoxb5a have already been implicated as direct targets of RA signaling ([Bruce et al., 2001], [Grandel et al., 2002], [Oosterveen et al., 2003] and [Sharpe et al., 1998]). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Conditions: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Bud to 5-9 somites |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 15(6), Waxman, J.S., Keegan, B.R., Roberts, R.W., Poss, K.D., and Yelon, D., Hoxb5b acts downstream of retinoic Acid signaling in the forelimb field to restrict heart field potential in zebrafish, 923-934, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell