|
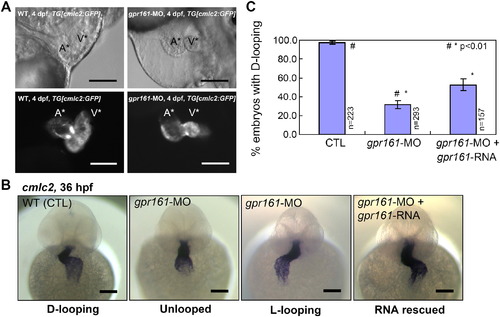
gpr161 knockdown disrupts cardiac looping morphogenesis. (A) Lateral view of zebrafish hearts at 4 dpf. Control and gpr161 knockdown in transgenic zebrafish embryos with cardiac specific GFP, TG[cmlc2:GFP], showing images of bright field (top panels) and fluorescent (bottom panels). A* labelled atrium, V* labelled ventricle. (B) Cardiac looping morphogenesis marked by cmlc2 expression in control (D-looping), gpr161 knockdown (unlooped and L-looping) and RNA rescued embryos. All scale bars were 100 μm. (C) Graphical summary of gpr161 knockdown disrupted normal cardiac D-looping morphogenesis at 36 hpf. Calculation as % of embryos with D-looping in control (97.8 ± 1.3%; n = 223), embryos injected with gpr161 morpholino (MO#36, 32.4 ± 4.1%; n = 293) and RNA rescue (gpr161 RNA without 5′UTR; 52.2 ± 3.4%; n = 157), n was number of total embryos and results were from 4 injection experiments. Error bars were ± SEM. t-test * and # indicated statistical significance, p < 0.01.
|