Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-081003-27
- Publication
- Yoshida et al., 2008 - Zebrafish orthologue of mental retardation protein IL1RAPL1 regulates presynaptic differentiation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
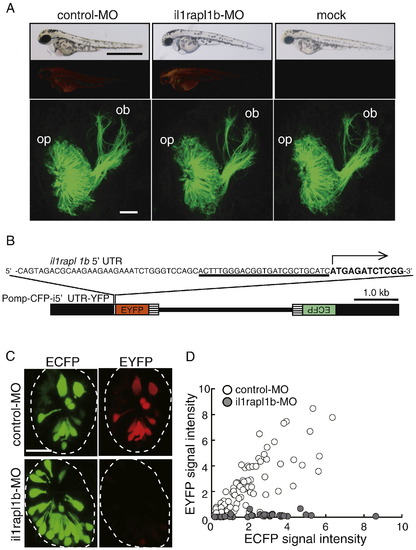
Evaluation of morpholino-mediated protein knockdown. (A) The lateral views of whole zebrafish bodies (top row panels), their lissamine fluorescent signals to monitor the distribution of morpholino oligonucleotides (second row panels) and frontal views of the olfactory placode and bulb (bottom row panels) of control-MO (left panels)-, il1rapl1b-MO (middle panels)-and mock (right panels)-injected embryos carrying the omp promoter-driven tau-EGFP transgene at 60 hpf. Dorsal is to the top and medial is to the right for the bottom panels. Bar = 1 mm for top row panels and 20 μm for bottom row panels. op, olfactory placode; ob, olfactory bulb. (B) Structure of Pomp-CFP-i5′UTR-YFP vector for the evaluation of il1rapl1b-MO-mediated protein knockdown. The target sequence for il1rapl1b-MO is underlined and translation initiation site is indicated as an arrow. Black boxes, the omp promoter; hatched boxes, SV40 polyadenylation signal sequence; lines, pBluescript II SK+. (C) ECFP (left panels) and EYFP (right panels) signals in the olfactory placode of embryos injected with Pomp-CFP-i5′UTR-YFP vector and control-MO (upper panels) and with Pomp-CFP-i5′UTR-YFP vector and il1rapl1b-MO (lower panels) at 84 hpf. (D) ECFP and EYFP fluorescent intensity of individual olfactory neurons in control morphants (open circles) and il1rapl1b morphants (gray circles) at 84 hpf are plotted. n = 79 and 35 for 5 control morphants and 4 il1rapl1b morphants, respectively. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Pec-fin to Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 39(2), Yoshida, T., and Mishina, M., Zebrafish orthologue of mental retardation protein IL1RAPL1 regulates presynaptic differentiation, 218-228, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.