Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080723-6
- Publication
- Udvadia, 2008 - 3.6kb Genomic sequence from Takifugu capable of promoting axon growth-associated gene expression in developing and regenerating zebrafish neurons
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
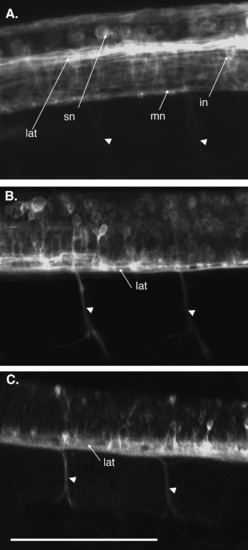
Transgene expression in spinal neurons is developmentally regulated. Lateral view of maximum projections of confocal stacks taken through tg(3.6fgap43:GFP)SA1 spinal cord at 24, 48, and 96 hpf. (A) Motorneurons (mn), interneurons (in), and sensory neurons (sn), as well as logitudinal axonal tracts (lat) are observed at 24 hpf. Signal from axons of motorneurons exiting the spinal cord is weak, but increases over time as the number of axons increase (arrowheads). (B) GFP-expressing cell bodies are observed throughout the dorso-ventral axis of the spinal cord, and axons of motorneurons (arrowheads) are observed exiting the spinal cord at 48 hpf. (C) By 96 hpf, expression in the cell bodies of spinal neurons is diminished, but longitudinal axonal tracts and axons of motorneurons exiting the spinal cord continue to express GFP. Arrowheads indicate motorneuron axons exiting the spinal cord. Scale bar = 100 μm. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Day 4 |
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 8(6), Udvadia, A.J., 3.6kb Genomic sequence from Takifugu capable of promoting axon growth-associated gene expression in developing and regenerating zebrafish neurons, 382-388, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns