Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080521-8
- Publication
- Zhang et al., 2001 - A dual role for the zebrafish unplugged gene in motor axon pathfinding and pharyngeal development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
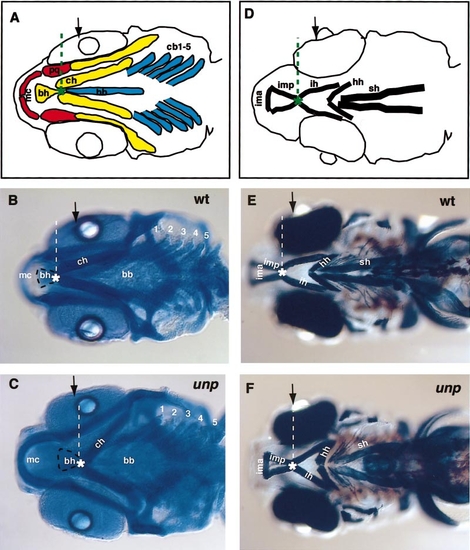
Pharyngeal arch defects in unplugged larvae. (A) Schematic drawing of pharyngeal arch cartilages. The components of the mandibular arch are labeled in red, the hyoid arch in yellow and the five branchial arches in blue. Note that not all cartilage components are indicated, and that only the distal portions of the branchial arches are outlined. The contact point (green asterisk) between the ceratohyals (ch) and the basihyal (bh) is located anterior to the lens (black arrow). (B, C) Five-dpf wild-type and unplugged mutant larvae stained with Alcian blue. (B) In wild-type larvae, the contact point between the basihyal (outlined by a black dashed line) and the ceratohyals (white asterisk) is located anterior to the lens (black arrow). Note that Meckel?s cartilages are situated further dorsally than the six posterior arches, and therefore appear slightly out of focus. (C) In unplugged mutants, Meckel?s cartilages (mc) are displaced ventrally to the same dorso-ventral position as the posterior arches, and now appear in the same focal plane. Also, the basihyal and the anterior end of the ceratohyals are shifted more posteriorly. As a result, the basihyal now contacts the ceratohyals at the level of the lens (dashed line). (D) Schematic representation of pharyngeal muscles. Note that the contact point (green asterisk) between the interhyal (ih) muscle and the intermandibularis posterior (imp) muscle is located anterior to the lens (black arrow). (E, F) Five-dfp wild-type and unplugged mutant larvae stained with the MF-20 antibody for pharyngeal muscles. Note that in wild-type larvae, the interhyal (ih) muscle contacts the intermandibularis posterior (imp) muscle at a level anterior the lens (black arrow). In unplugged mutant larvae, the interhyal (ih) muscle contacts the intermandibularis posterior (imp) muscle at a more posterior position, at level of the lens (black arrow in F). Abbreviations: bb, basibranchials; bh, basihyal; cb1-5, ceratobranchial 1-5; ch, ceratohyal; hh, hyohyal; ih, interhyal; ima, intermandibularis anterior; imp, intermandibularis posterior; mc, Meckel?s cartilage; pq, palatoquadrate; sh, sternohyoideus. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 240(2), Zhang, J., Malayaman, S., Davis, C., and Granato, M., A dual role for the zebrafish unplugged gene in motor axon pathfinding and pharyngeal development, 560-573, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.