Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080513-15
- Publication
- Herbomel et al., 2001 - Zebrafish early macrophages colonize cephalic mesenchyme and developing brain, retina, and epidermis through a M-CSF receptor-dependent invasive process
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
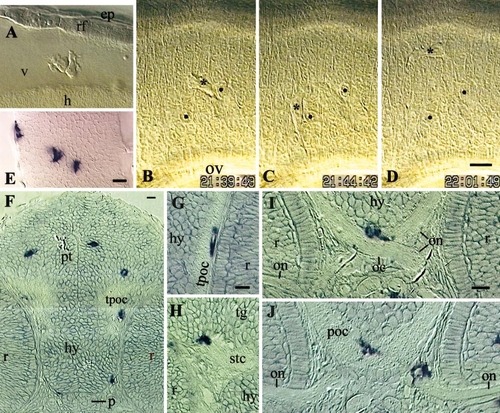
Early macrophages in the brain. (A?D) Live embryos, 35 hpf, lateral view, rostral to the left. (A) Two macrophages in the fourth brain ventricle, dorsal to the first somite. (B?D) Three instants of the macrophage wandering in hindbrain rhombomere 5 (shown in movie 2; asterisk, macrophage nucleus; two neuroepithelial cell nuclei labeled by black dots serve as reference points; time indicated in h, min,s. (E?J) In situ hybridization for L-plastin. (E) 35 hpf, hindbrain, left half, dorsal view, rostral upward. (F?J) Resin cross sections, 48 hpf. (F) Section through the pretectum (pt), hypothalamus, and pituitary (p). (G) Macrophage in the tract of the post-optic commissure (TPOC). (H) Macrophage partly in the tegmentum (tg), partly in the sub-tegmental commissure (stc). (I, J) Two successive sections, in rostro-caudal order, showing one macrophage bridging the optic chiasm (oc) and post-optic commissure (poc) (I, J), and another one in the mesenchyme, riding on the optic nerve (J). (h) hindbrain wall; (v) fourth ventricle; (rf) roof of the fourth ventricle; (ep) epidermis; (ov) otic vesicle, (hy) hypothalamus, (tpoc) TPOC, (r) retina, (on) optic nerves. Bars, 10 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 238(2), Herbomel, P., Thisse, B., and Thisse, C., Zebrafish early macrophages colonize cephalic mesenchyme and developing brain, retina, and epidermis through a M-CSF receptor-dependent invasive process, 274-288, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.