Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080501-19
- Publication
- Zeller et al., 2002 - Migration of zebrafish spinal motor nerves into the periphery requires multiple myotome-derived cues
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
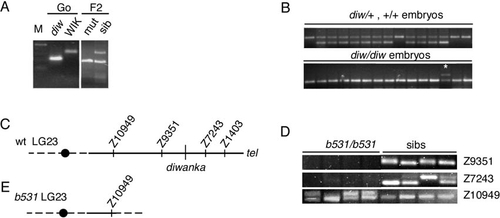
The diwanka locus maps on LG 23 and is deleted in b531 mutant embryos. (A) PCR amplification using marker z1403 and DNA isolated from the G0 diwanka Tü fish, the G0 WIK fish, pooled F2 mutants, and pooled F2 siblings. The Tü-specific PCR fragment is shorter than the WIK-specific fragment. Amplification with z1403 in the F2 sibling pool DNA results in a Tü-specific and a WIK-specific fragment, while in DNA from pooled mutant only the Tü-specific fragment is present (higher mobility), indicating linkage between z1403 and the diwanka mutation. (B) PCR amplification using marker z1403 and DNA from individual F2 sibling embryos (top). (Bottom) PCR amplification using marker z1403 and DNA from individual F2 diwanka mutant embryos. In a recombinant embryo, a Tü-specific and a WIK-specific fragment are present (*). (C) Schematic representation of LG 23 around the diwanka locus. A black circle indicates the centromere. (D) PCR amplification of SSLP markers from DNA of four b531/b531 mutant embryos and four sibling embryos. In sibling embryos (sibs), all tested markers are present. In the four b531/b531 embryos, marker z10949 is present, while markers z9351 and z7243 are absent. (E) Schematic representation of LG 23 in b531/b531 embryos. In these embryos, LG 23 breaks between z10949 and z9351, deleting the remaining chromosomal arm, including the diwanka locus. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 252(2), Zeller, J., Schneider, V., Malayaman, S., Higashijima, S., Okamoto, H., Gui, J., Lin, S., and Granato, M., Migration of zebrafish spinal motor nerves into the periphery requires multiple myotome-derived cues, 241-256, Copyright (2002) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.