Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080411-22
- Publication
- Insinna et al., 2008 - The homodimeric kinesin, Kif17, is essential for vertebrate photoreceptor sensory outer segment development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
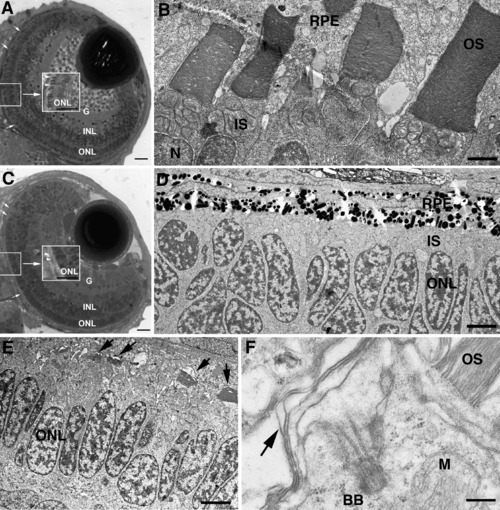
Disrupted photoreceptor OS formation in Kif17 morphants. (A) WT eye of a 3-day-old embryo. The lens and retinal lamination are well developed. OSs (small arrows, center inset) have developed throughout the retina. G, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer (photoreceptor nuclei). Bar = 10 μm. (B) EM view of junction between photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in WT showing mitochondria rich inner segments (IS) and the lamellar OSs; N, photoreceptor nucleus. Bar = 2.5 μm. (C) Morphant eye of a 3-day-old embryo shows normal retinal lamination but lack of OS (small arrow, center inset). Bar = 10 μm. (D) EM view of junction between photoreceptors and RPE in a morphant; IS layer is visible between nuclei (ONL) and RPE, but OS are not present. Bar = 5 μm. (E) EM view of junction between photoreceptors and RPE of a morphant with short, under-developed OS (arrows). Bar = 6.6 μm. (F) High power EM view of a photoreceptor showing the basal body (BB) at the base of the cilium; arrow indicates disorganized OS discs. M, mitochondrion. OS (upper right) is from an adjacent photoreceptor. Bar = 0.5 μm. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 316(1), Insinna, C., Pathak, N., Perkins, B., Drummond, I., and Besharse, J.C., The homodimeric kinesin, Kif17, is essential for vertebrate photoreceptor sensory outer segment development, 160-170, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.