|
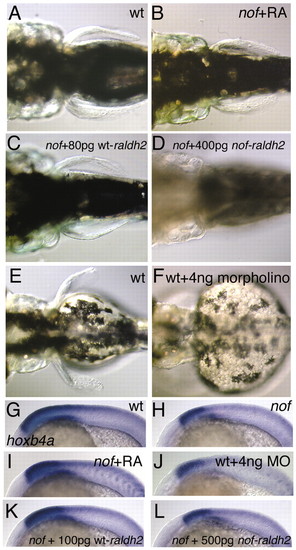
Dorsal view of pectoral fins on day 5 in (A) a wild-type larva and (B) a nof homozygote after treatment with retinoic acid (10?9 M, 30% epiboly until 16 hours) and (C) after injection of wild-type raldh2 mRNA on day 6. (D) Injection of nof raldh2 mRNA does not provoke fin development in nof mutants. (E,F) Pectoral fins on d3 are prominent in wild type (E) but do not develop after injecting a raldh2-specific morpholino oligonucleotide (F). hoxb4a expression at 20s in wild-type (G) and (H) nof sibling embryos. (J,L) Similar hoxb4a expression levels as in nof homozygotes are detected upon injection of raldh2-specific morpholino into wild-type embryos (J) and upon injection of 500 pg mRNA derived from the nof-allele of raldh2 into nof homozygotes (L). (I,K) Increase of hoxb4a expression levels upon treatment of nof homozygotes (I) with retinoic acid (10?9 M; 30% until 20s) and (K) injection of 100 pg of wild-type raldh2 mRNA.
|