Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-060303-16
- Publication
- Pogoda et al., 2006 - The proneural gene ascl1a is required for endocrine differentiation and cell survival in the zebrafish adenohypophysis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
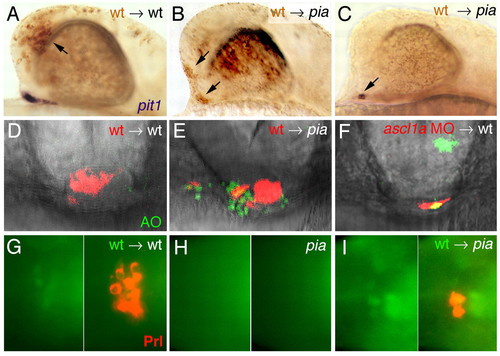
Ascl1 is required cell autonomously to promote pit1 expression, cell survival and Prl production. (A-C) Lateral views on chimeric embryos at 26 hpf embryos, in situ hybridized for pit1 transcripts in blue and with transplanted wild-type cells in brown (indicated with arrows). (A) Wild-type control recipient with wild-type donor cells in the telencephalon and normal pit1 expression. (B) pia recipient with wild-type cells in eyes, telencephalon and ventral regions of diencephalon, lacking adenohypophyseal pit1 expression. (C) pia embryo with few wild-type cells within adenohypophyseal domain, showing pit1 expression in these wild-type cells only. (D-F) Frontal views of pituitaries at 32 hpf. Nomarski images superimposed with red fluorescence revealing transplanted cells; green fluorescence revealing Acridine Orange (AO)-positive cells. (D) Wild-type control recipient with AO-negative wild-type donor cells in the pituitary. (E) pia recipient, with AO-negative transplanted wild-type cells (red), but many AO-positive host cells (green) in pituitary. (F) Wild-type recipient, with one AO-positive (yellow) and two AO-negative ascl1a morphant donor cells in pituitary. (G-I) Ventral views of pituitaries at 48 hpf, anterior towards the left. Left panels show transplanted h2a::h2a-GFP transgenic cells weakly labeled in green, right panels an overlay of the same images with anti-Prl immunostaining in red. (G) Wild-type host; (H) pia host without transplanted cells in pituitary; (I) pia host with three wild-type cells in pituitary, two of which produce Prl protein. |