Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-051025-4
- Publication
- Flanagan-Steet et al., 2005 - Neuromuscular synapses can form in vivo by incorporation of initially aneural postsynaptic specializations
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
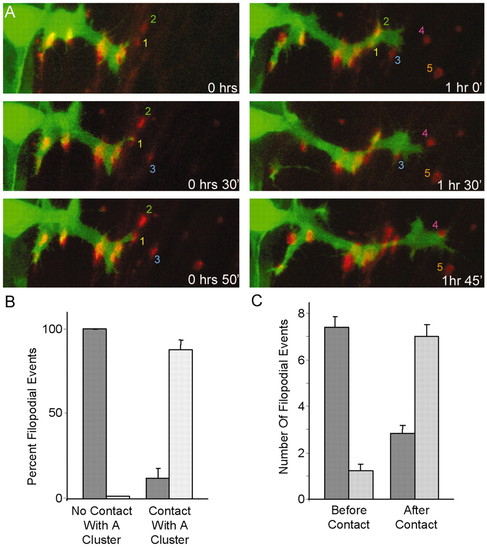
CaP axonal behavior changes following contact with AChR clusters. (A) HB9:GFP-labeled CaP reorients its growth repeatedly following contact of its growth cone with clusters. Colored numbers 1-5 indicate initially aneural clusters that growth cones contact. (B) Most of the filopodia that contact an AChR cluster are retained (light bars) until the end of the imaging period, whereas most of those that do not make contact retract (dark bars). (n=173 filopodia from 13 cells in seven animals; P<0.0001 for both groups.) (C) Filopodial activity is lower in the quadrant surrounding the central band of AChRs (light bars) than in the sum of the other three quadrants (dark bars), prior to the initial contact of a filopodium with a cluster. After the first filopodium contacts a cluster, however, more filopodia extend in the quadrant containing the end-plate band than in the other three quadrants together (n=1022 filopodia from 10 cells in five fish; P<0.0001 both before and after contact). |