Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-051013-5
- Publication
- Mavropoulos et al., 2005 - sox4b is a key player of pancreatic alpha cell differentiation in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
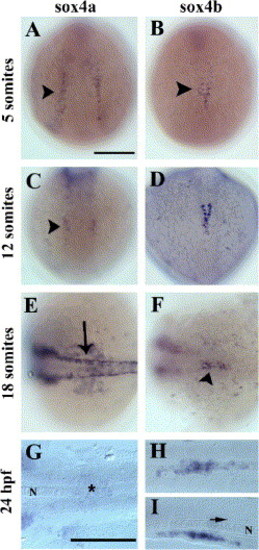
Expression of sox4a and sox4b genes during zebrafish development. Whole-mount in situ hybridization with sox4a- (left panels) and sox4b- (right panels) digoxigenin-labeled anti-sense probes at various stages of zebrafish development (from the 5-somite stage to 24 hpf). (A?D) Dorsal views, anterior to the top. (E, F) Dorsal views, anterior to the left. (G?I) dorsal views (G, H) and lateral view (I) with anterior to the left of yolk-free embryos. A scale bar = 200 μm, G scale bar = 200 μm in G, H, and I. Arrowhead in panel B: mid-trunk endoderm. Arrow in panel E: dorsal neural tube; arrow in panel I: floor plate. The notochord (N) is indicated in panels G and I. As soon as the 5-somite stage (B), sox4b starts to be expressed in some scattered cells of the mid-trunk endoderm (arrowhead). As somitogenesis goes on, the expression persists in this region (D, F arrowhead) until 24 hpf (H, I). By contrast, sox4a is expressed in various tissues such as the lateral plate mesoderm (A, arrowhead), the hindbrain (C, arrowhead), the neural crest (E, arrow) but expression in the pancreatic region is hardly above the detection limit (G, star). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | 5-9 somites to Prim-5 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 285(1), Mavropoulos, A., Devos, N., Biemar, F., Zecchin, E., Argenton, F., Edlund, H., Motte, P., Martial, J.A., and Peers, B., sox4b is a key player of pancreatic alpha cell differentiation in zebrafish, 211-223, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.