Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-050201-1
- Publication
- D'Souza et al., 2005 - Formation of the retinotectal projection requires Esrom, an ortholog of PAM (protein associated with Myc)
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
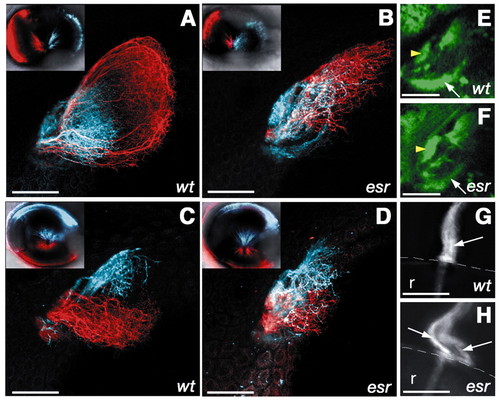
The retinotectal projection in the esrom mutant. (A-D) Optic tectum of 4-day-old zebrafish, with retinal axons labeled using DiI (red) or DiD (blue). Insets show lateral view of the injected eye. (A) Axons from the anterior region of the eye (red) project to the posterior tectum in wild type. Axons from the posterior (blue) arborize in the anterior tectum. (B) In the esrom mutant, anterior axons defasciculate and arborize anteriorly. (C) Axons from the ventral (red) and dorsal (blue) regions of the eye are well separated in a wild type. (D) In the mutant, there is some overlap between two populations. (E,F) Dorsal view of the pretectal region of 3-day-old fish, in which retinal axons are labeled with GFP under the sonic hedgehog promoter. The pretectal target AF7 (yellow arrowhead) is more innervated in the mutant (F) compared with the wild type (G). AF9 (arrow), by contrast, is less innervated in the mutant. (G,H) The optic nerve exiting from the eye in 7-day-old fish. Only dorsal neurons have been labeled with DiI. In the wild type (G), axons remain closely associated with one another in the optic nerve (arrow). In the mutant (H), axons have formed two separate bundles (arrows). Scale bar: 50 Ám. Anterior is towards the left. r, retina; the broken white line in G,H indicates the margin of the eye. (E,F) Single optical planes; other panels are projections of z-stacks. |