Fig. 9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-050124-5
- Publication
- Kozlowski et al., 2005 - The zebrafish dog-eared mutation disrupts eya1, a gene required for cell survival and differentiation in the inner ear and lateral line
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
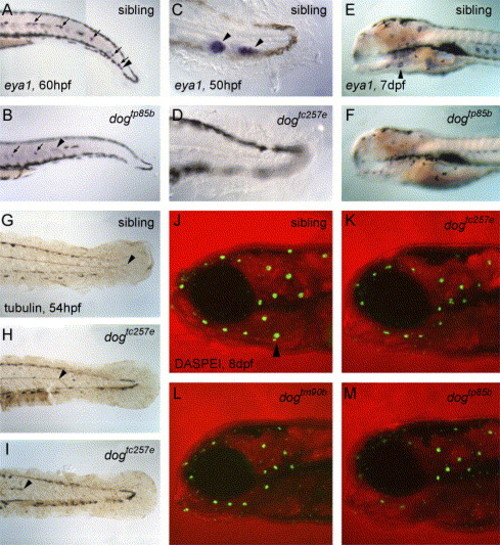
Lateral line phenotype in dog alleles. (A) Expression of eya1 mRNA in posterior lateral line neuromasts (arrows) of a phenotypically normal sibling embryo at 60 hpf. Migration of the posterior lateral line primordium (arrowhead) is complete. (B) In the tail of a dogtp85b mutant, eya1 is expressed in the nascent neuromasts (arrows), but the primordium has not reached the tail tip (arrowhead). (C and D) Higher magnification view of eya1 expression at the tip of the tail at 50 hpf. eya1 is strongly expressed in the primordium and neuromast (arrowheads) in the wild-type sibling embryo, but no eya1-expressing lateral line cells have reached the tail tip in the dogtc257e mutant. (E and F) By 7 dpf, eya1 is still strongly expressed in all neuromasts in the wild-type sibling. Expression is weaker in the dogtp85b mutant, and neuromasts of the opercular line (arrowhead) are missing. (The eyes have been removed for clarity.) (G, H, and I) Dissected preparations of tail skin from 54-hpf embryos stained as whole mounts with an antibody to acetylated tubulin showing the extent of the posterior lateral line nerve. In the dogtc257e mutant, the nerve terminates before the tail tip. (J?M) Confocal images of live embryos stained with the vital dye DASPEI showing hair cells in the neuromasts of the anterior lateral lines (green dots). In all three dog alleles, the neuromasts have fewer hair cells than normal, and neuromasts of the opercular line (arrowhead) are missing. Note also the rounded shape of the jaw in all three dog alleles. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage Range: | Pec-fin to Days 7-13 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 277(1), Kozlowski, D.J., Whitfield, T.T., Hukriede, N.A., Lam, W.K., and Weinberg, E.S., The zebrafish dog-eared mutation disrupts eya1, a gene required for cell survival and differentiation in the inner ear and lateral line, 27-41, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.