- Title
-
Jaw and branchial arch mutants in zebrafish. I. Branchial arches
- Authors
- Schilling, T.F., Piotrowski, T., Grandel, H., Brand, M., Heisenberg, C.P., Jiang, Y.J., Beuchle, D., Hammerschmidt, M., Kane, D.A., Mullins, M.C., van Eeden, F.J., Kelsh, R.N., Furutani-Seiki, M., Granato, M., Haffter, P., Odenthal, J., Warga, R.M., Trowe, T., and Nüsslein-Volhard, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
Mutant phenotypes in living larvae. Lateral views at 6 days. Arrows indicate branchial arches, P3-P7, which are reduced in all of these mutants. Arrowheads indicate the lower jaw. (A) wild type, wt. The jaw extends anterior to the eye and gill filaments of the branchial arches, lined with blood vessels, protrude ventral to the otic vesicle (ot). (B) lowts213. The jaw is shifted ventrally and some gill filaments remain. (C) flatf21c. Gills are severely reduced. (D) babtb210c. The head is severely reduced, the jaw does not extend and gills are absent. (E) sertk18c. The jaw is reduced, the mouth hangs open and gills are slightly reduced. (F) factu45b. Only gills are reduced. (G) tq235. All arches are absent and the mouth is displaced posteriorly. (H) daktw25. All arches are shorter and wider than normal and the jaw is displaced posteriorly. (I) boxtm70g. The jaw hangs slightly and gills are reduced. |
|
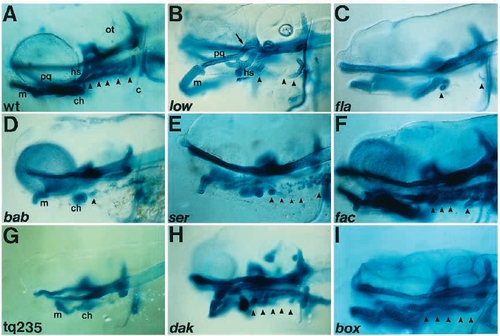
Skeletal defects in mutants (lateral view). Cartilage in 6-day-old larvae is stained with Alcian blue and whole-mounted. Arrowheads indicate the positions of branchial arches. (A) Wild type, wt. There are five branchial arches, P3-P7. (B) low. Two branchial arches, P4 and P5, are absent. Meckel?s cartilage hangs ventrally, the hyosymplectic is reduced and the palatoquadrate makes ectopic contact with the neurocranium (arrow). (C) fla. Branchial arches P4-P6 are absent. (D) bab. All branchial arches are absent except the basibranchial of P3. Meckel?s cartilage hangs ventrally and the ceratohyal is reduced. The neurocranium is severely reduced. (E) ser. One branchial arch, P6, is absent. The ceratobranchial of P3 and basibranchials of P4 and P5 are present, as is a single tooth of P7. (F) fac. P6 is absent. (G) tq235. All branchial arches are absent. Anterior arches and the neurocranium are severely reduced. (H) dak. All branchial arches are reduced. Meckel?s cartilage hangs ventrally. (I) box. All branchial arches are reduced. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
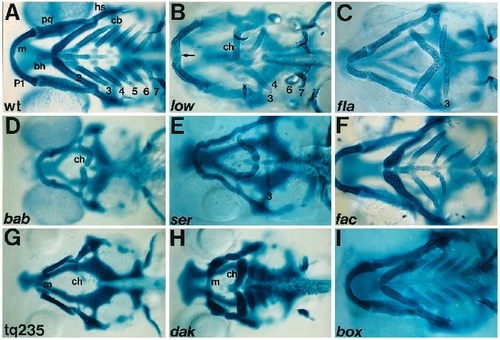
Skeletal defects in mutants (ventral view; pharyngeal arches). (A) Wild type, wt. The seven arch segments contain 13 bilateral and 6 midline cartilages. (B) low. The ceratohyal and ceratobranchials are reduced, P5 is absent. P7, including teeth, is well developed. Meckel?s cartilages fuse in the midline (arrow). (C) fla. All arches are reduced. Meckel?s cartilages are narrow and pointed. Ceratohyals point posteriorly and contact ceratobranchials of P3. There are single teeth on P7. (D) bab. Branchial arches are absent except the basibranchial of P3. Anterior arches are reduced, ceratohyals kinked and posteriorly displaced. (E) ser. Ceratobranchials of P4-P7 are absent; basibranchials are present. Anterior arches are reduced, ceratohyals kinked and posteriorly displaced. (F) fac. Branchial arches, P4-6, are reduced. (G) tq235. Branchial arches are absent. Anterior arches are severely reduced. (H) dak. All arches are abnormally short and wide, narrowing medially. (I) box. All arches are shorter and wider than wt. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Skeletal defects in mutants (ventral view; neurocranium). A more dorsal focus of the animals shown in Fig. 4. (A) Wild type, wt. (B) low. The ethmoid plate is split in the midline (arrow). (C) fla. The ethmoid plate is narrow. (D) bab. All cartilages are severely reduced, including parachordal cartilages (arrow). (E) ser. (F) fac. (G) tq235. All cartilages are severely reduced, particularly the ethmoid plate. (H) dak. All cartilages short and thick. (I) box. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|