- Title
-
Tau accumulation is cleared by the induced expression of VCP via autophagy
- Authors
- Giong, H.K., Hyeon, S.J., Lee, J.G., Cho, H.J., Park, U., Stein, T.D., Lee, J., Yu, K., Ryu, H., Lee, J.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Acta Neuropathol.
|
The clearance of Tau protein in a zebrafish TAU-overexpressing transgenic model coincides with the increased autophagy activity. a The construct used for the Tau transgenic line that overexpress human TAUP301L and mCherry connected by a self-cleaving 2A peptide under the control of the zebrafish elavl3 promoter and a representative image of zebrafish larvae at 2 dpf. Scale bars = 500 ?m. b Semi-quantitative RT-PCR run on agarose gel shows that human TAU mRNA was steadily expressed at 1, 3, 5, 7 dpf in the Tau tg line. c Western blots with antibodies against total Tau (T46), pTau (AT180, PHF, AT8) and autophagy markers (LC3, p62) for the Ctrl and Tau tg lines at 28 hpf, 2 and 5 dpf. d, e Densitometry measurement of triple biologic replicates of western blots using T46 (d) or p62 (e) antibodies in (c). f Gene expression changes of pro-inflammatory cytokines il6 and tnf-? at 1, 2, and 4 dpf. Data represent mean ▒ SEM, n = 3 (three biologic replicates), ANOVA test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005; ns, not significant. a.u. arbitrary unit |
|
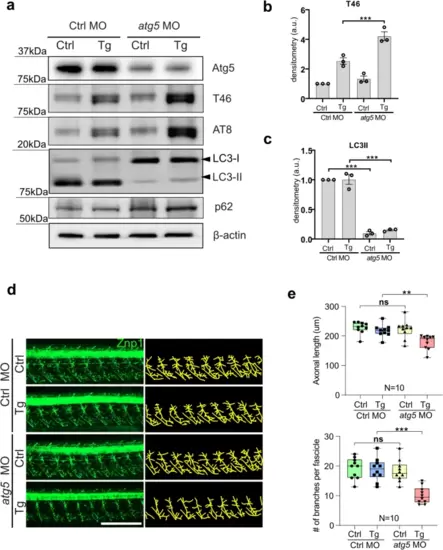
Autophagy inhibition by atg5 depletion reveals tau toxicity in the Tau tg line. a Western blots of Ctrl and atg5 morphants at 2 dpf. atg5 morphants exhibited accumulation of LC3-I and p62 as well as total Tau and pTau (T46 and AT8). b, c Densitometry measurement of triple biologic replicates of western blots using T46 (b) or anti-LC3 (c) antibodies in (a). d Representative confocal images of primary motor axons of Ctrl and atg5 morphants of the Ctrl and Tau tg lines at 2 dpf by Znp1 immunostaining (left panels) and tracing of motor axons for quantitation using images J (right panels). e Both lengths and branches numbers of motor axons were significantly reduced in atg5 morphants of the Tau tg line, but not in Ctrl. Data represent mean ▒ SEM, n = 10 (10 individual animals), ANOVA test, **p < 0.01; ns not significant, Scale bar = 200 Ám |
|
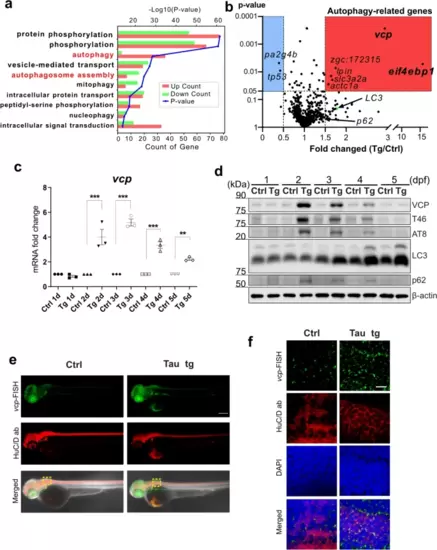
VCP induction correlates with Tau overexpression and clearance. a Top ten GO of DEGs from the comparative transcriptomic analysis of the Tau tg vs the Ctrl line. b A volcano plot of autophagy-related DEGs, identifying vcp and eif4ebp1 as the most significant DEGs with highest p value or fold change. c mRNA expression profile of vcp from 1 to 5 dpf by quantitative RT-PCR. d Western blots with antibodies against Vcp, total Tau (T46), pTau (AT8) and autophagy markers (LC3, p62) for the Ctrl and Tau Tg lines from 1 to 5 dpf. e Whole-mount co-staining of anti-HuC antibody and vcp mRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). f Enlarged view of yellow boxes in (e). Student t test, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005, Scale bar (in e and f) = 50 Ám |
|
VCP is required for autophagy-mediated Tau clearance. a Western blots of VCP, total Tau (T46) and pTau (AT8) of vcp MO and mRNA-injected embryos. vcp MO knockdown resulted in accumulation of Tau proteins, which was rescued by human VCPWT overexpression but not by mutant human VCPDKO. b Representative confocal images and the quantification of primary motor axons of vcp morphants and VCP mRNA expression in (a) at 2 dpf, visualized by Znp1 immunostaining (left panels) and tracing of motor axons for quantitation using images J (right panels). vcp knockdown showed more than ~ 50% reduction in both length and branching numbers of primary motor axons, which were partially rescued by VCPWT expression but not by mutant VCPDKO. c The diagram shows mutations in VCP protein construct; western blots of VCP, total Tau (T46), pTau (AT8) and autophagy marker (LC3, p62) antibodies of vcp MO and mRNA-injected embryos. vcp MO knockdown resulted in accumulation of Tau proteins, which was rescued by human VCPWT and VCPD395G overexpression but not by VCPDKO, VCPA232E, or VCPR155H. d Representative confocal images and the quantification of primary motor axons of vcp morphants and VCP mRNA expression in (c) at 2 dpf, visualized by Znp1 immunostaining (left panels) and tracing of motor axons for quantitation using images J (right panels). vcp knockdown showed more than ~ 50% reduction in both length and branching numbers of primary motor axons, which were partially rescued by VCPWT and VCPD395G expression but not by mutant VCPDKO, VCPA232E, or VCPR155H. Data represent mean ▒ SEM, n = 10 (10 individual animals), ANOVA test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005; Scale bar = 200 Ám |
|
VCP-dependent Tau clearance via autophagy pathway is conserved in mice. a Experimental scheme of AAV-pSyn1-TauP301L, AAV-pSyn1-VCP, and chloroquine (CQ) delivery into the hippocampus of WT mice (9-month-old). b LC3 and pTau (S202/T205) by AT8 immunostaining was performed in the hippocampus of each mouse group injected with AAV- pSyn1-Control, AAV-pSyn1-TauP301L, AAV-pSyn1-TauP301L + AAV-pSyn1-VCP and AAV-pSyn1-TauP301L + AAV-pSyn1-VCP + CQ, respectively. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. White dotted lines indicate the shape of neurons. Scale bars (white) = 10 ?m. c LC3 and pTau intensity was significantly increased in TauP301L group compared to the Control group. VCP overexpression significantly decreased pTau level in TauP301L + VCP group compared to TauP301L group. CQ injection significantly increased the levels of LC3 and pTau. d An experimental flow of passive avoidance behavior test in mice after the injection with AAV-pSyn1-Control, AAV-pSyn1-TauP301L, AAV-pSyn1-TauP301L + AAV-pSyn1-VCP, and AAV-pSyn1-TauP301L + AAV-pSyn1-VCP + CQ. e Latency to dark room was significantly rescued in TauP301L + VCP group compared to TauP301L group. Whereas TauP301L + VCP + CQ-injected group showed a significant decrease of the time of latency to dark room compared to TauP301L + VCP group. Significance at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005 by Student?s t test. Data are presented as mean ▒ SEM. n = 4 (10 individual animals) |
|
VCP immunoreactivity is decreased in the cortices of AD patients. a VCP Immunoreactivity was decreased while p-Tau (S202/T205) immunoreactivity was increased in the cortical neurons of AD patients compared to normal subject. The nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin. Arrowheads (white) indicate neurons. Scale bars = white, 20 ?m; black, 20 ?m. b The levels of VCP and p-Tau (S202/T205) were inversely correlated in the cortex of AD patients (N = 3) and control subjects (N = 3). c VCP mRNA expression level (normalized to GAPDH) was significantly decreased in the frontal cortices of AD patients (AD, N = 7) compared to control subjects (Ctrl, N = 7). d A schematic illustrating possible mechanisms by which increased autophagy induced by VCP in the presence of phosphorylated Tau. VCP may play an essential role in facilitating the autophagy flux for Tau clearance, potentially by the initiation of the autophagy (1), binding to LC3 (2), the fusion of the autophagosome and the lysosome (3), and/or enhanced lysophagy (4). See the main text for details. The diagram was created with BioRender.com. Student t test, **p < 0.01. Data are presented as mean ▒ SEM |