- Title
-
Macrophages inhibit extracellular hyphal growth of A. fumigatus through Rac2 GTPase signaling
- Authors
- Tanner, C.D., Rosowski, E.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Infect. Immun.
|
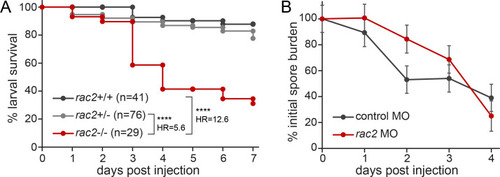
Rac2-deficient zebrafish larvae are susceptible to |
|
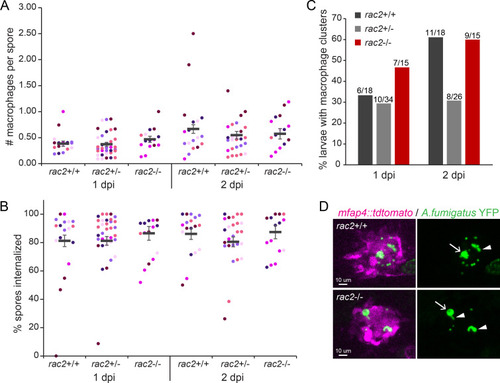
Rac2 is not required for macrophage migration to or phagocytosis of |
|
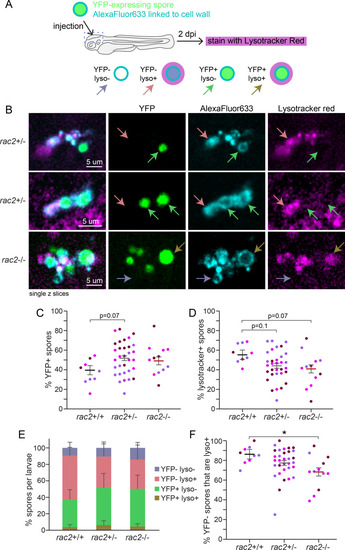
Rac2 is not required for spore acidification or killing. |
|
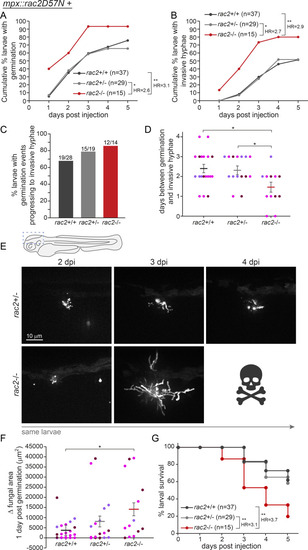
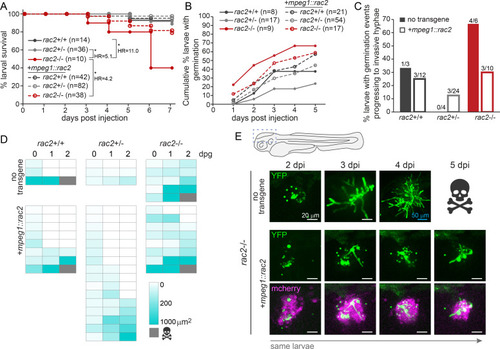
Macrophages control spore germination and extracellular hyphal growth through Rac2 function. |
|
Macrophage-expressed Rac2 is sufficient to promote host survival against invasive |