- Title
-
Gill developmental program in the teleost mandibular arch
- Authors
- Thiruppathy, M., Fabian, P., Gillis, J.A., Crump, J.G.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife
|
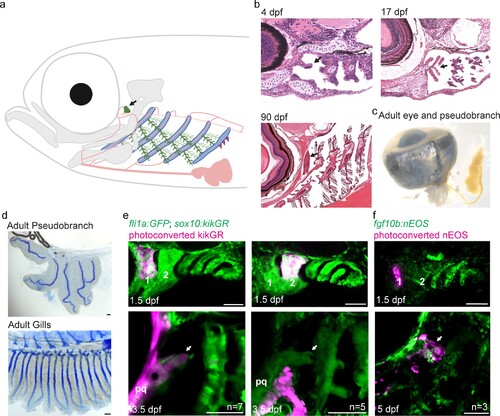
The zebrafish pseudobranch derives from mandibular arch mesenchyme and first pouch epithelia. (a), Schematic showing the pseudobranch (arrows), gill filaments (branched green structures) connected to gill bars (blue), teeth (purple), vasculature (pink), and jaw and jaw-support skeleton (gray). (b) Hematoxylin and Eosin-stained sections show emergence of the pseudobranch bud at 4 dpf (adapted from https://bio-atlas.psu.edu/zf/view.php?atlas=5&s=41), five filaments at 17 dpf (adapted from https://bio-atlas.psu.edu/zf/view.php?atlas=65&s=1738), and the fused pseudobranch at 90 dpf (adapted from https://bio-atlas.psu.edu/zf/view.php?atlas=29&s=312). (c) Dissected adult pseudobranch shows the ophthalmic artery connecting it to the eye. (d) Alcian staining shows five cartilage rods in the pseudobranch and similar cartilage in gill primary filaments. (e) Photoconverted kikGR-expressing mesenchyme (red) from the dorsal first arch (numbered) at 1.5 dpf contributes to the palatoquadrate cartilage (pq) and pseudobranch mesenchyme (arrow) at 3.5 dpf. Photoconverted dorsal second arch cells do not contribute to the pseudobranch. In green, fli1a:GFP labels the vasculature and neural crest-derived mesenchyme, with mesenchyme also labeled by unconverted sox10:kikGR. (f) In fgf10:nEOS embryos, photoconversion of first pouch endoderm (numbered) at 1.5 dpf labels the pseudobranch epithelium (arrow) at 5 dpf. n numbers denote experimental replicates in which similar contributions were observed. Scale bars, 50 µm. |
|
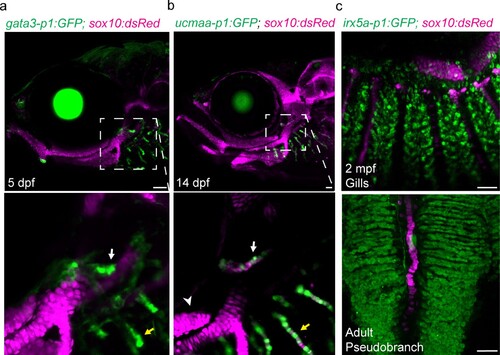
(a-c) In the pseudobranch (white arrows) and gill filaments (yellow arrows), gata3-p1:GFP labels growing buds, ucmaa-p1:GFP labels cellular cartilage (distinct from hyaline cartilage, arrowhead), and irx5a-p1:GFP labels pillar cells. sox10:dsRed labels cartilage for reference. Images in (b) and (c) are confocal projections, with magnified regions shown below in single sections for gata3-p1:GFP and ucmaa-p1:GFP. Scale bars, 50 µM.<
|
|
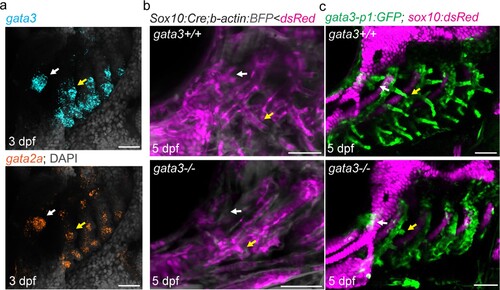
(a) Similar expression of gata3 and gata2a in developing pseudobranch (white arrows) and gill regions (yellow arrows). (b) Sox10:Cre; acta2:loxP-BFP-Stop-loxP-dsRed labels Cre-converted dsRed+ neural crest-derived mesenchyme (magenta) and unconverted BFP+ epithelia (gray). (c) gata3-p1:GFP labels pseudobranch and gill filament buds, and sox10:dsRed labels cartilage. For both (b) and (c), 3/3 gata3 mutants displayed reduced formation of the pseudobranch (white arrows) and gill filaments (yellow arrows), compared to 3 controls each. Scale bars, 50 µM.
|