- Title
-
Dopaminergic neurons regenerate following chemogenetic ablation in the olfactory bulb of adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Authors
- Godoy, R., Hua, K., Kalyn, M., Cusson, V.M., Anisman, H., Ekker, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
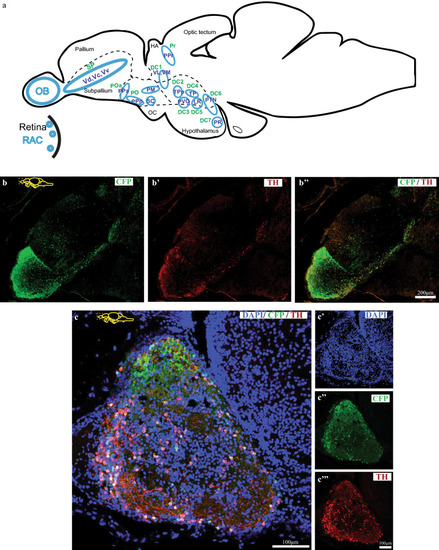
Expression of Tg(dat:CFP-NTR) in the adult zebrafish brain. ( |
|
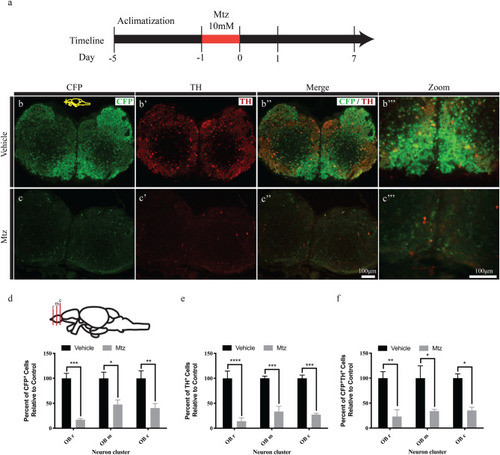
Ablation of DA neurons following Mtz treatment. ( |
|
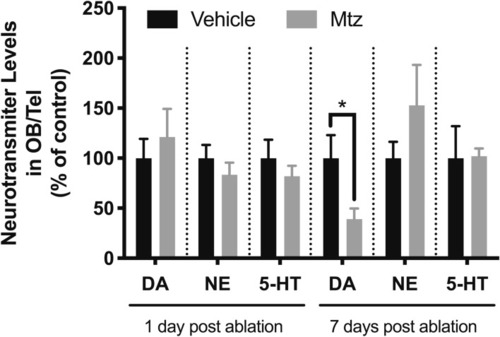
Decrease in neurotransmitter levels following ablation of dopaminergic neurons. Levels of dopamine (DA), serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE) were measured in dissected OB/telencephalon tissue, 1 or 7 days post-Mtz treatment. *( |
|
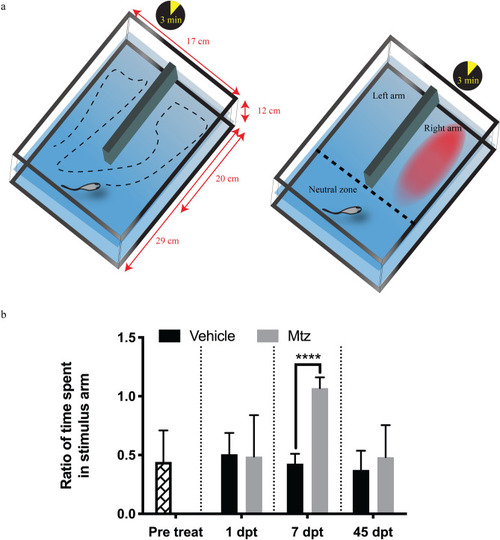
Decreased olfactory function following neuronal ablation. ( |
|
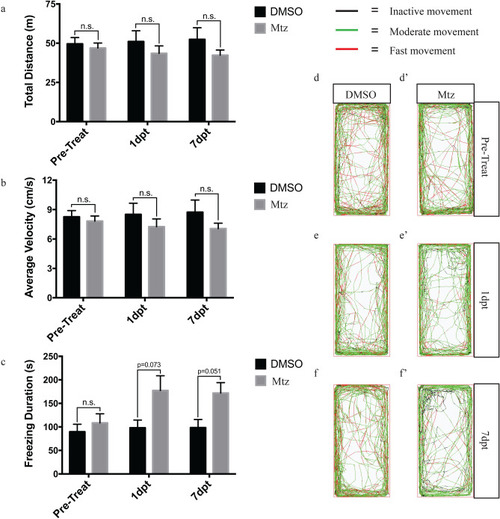
Relative swimming activity of Mtz and DMSO treated adult zebrafish |
|
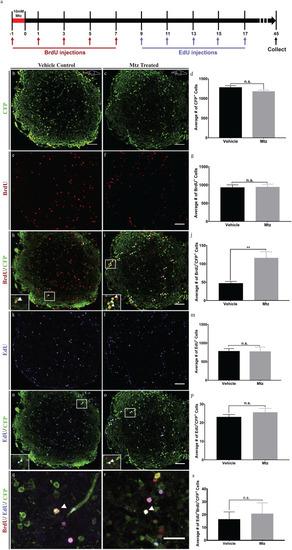
Formation of new CFP positive cells following neuronal ablation only occur before 9 days post ablation. ( |