- Title
-
Prokaryotic ribosomal RNA stimulates zebrafish embryonic innate immune system
- Authors
- Basu, A., Yoshihama, M., Uechi, T., Kenmochi, N.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Res. Notes
|
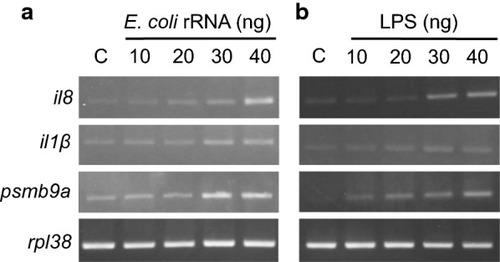
Dose-dependent increase in the expression levels of markers upon |
|
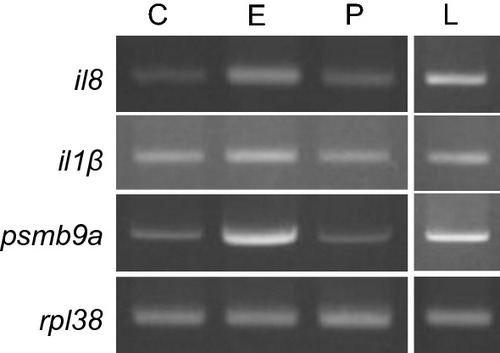
Comparative induction potential of |
|
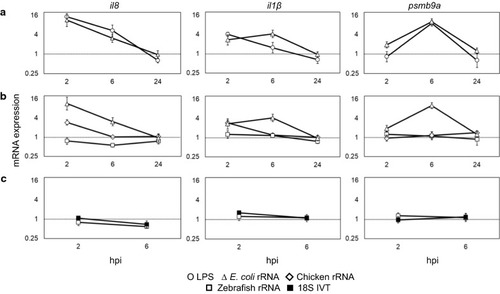
Comparative induction potentials of LPS; rRNAs from |