- Title
-
Zebrafish Carrying pycr1 Gene Deficiency Display Aging and Multiple Behavioral Abnormalities
- Authors
- Liang, S.T., Audira, G., Juniardi, S., Chen, J.R., Lai, Y.H., Du, Z.C., Lin, D.S., Hsiao, C.D.
- Source
- Full text @ Cells
|
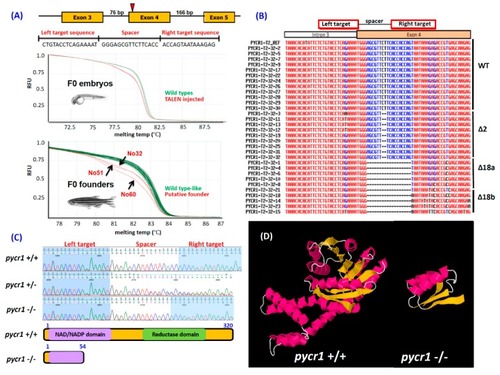
Generation of pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 ( |
|
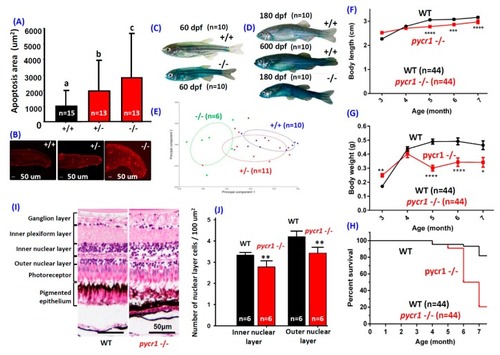
Morphologies of |
|
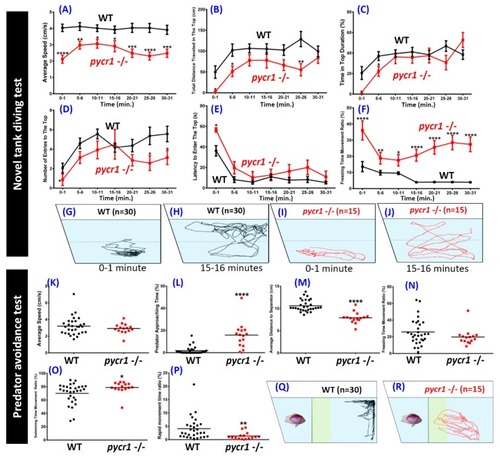
Comparison of behavioral endpoints in novel tank exposure test and predator avoidance test in wild type and PHENOTYPE:
|