- Title
-
Potentiation of P2RX7 as a host-directed strategy for control of mycobacterial infection
- Authors
- Matty, M.A., Knudsen, D.R., Walton, E.M., Beerman, R.W., Cronan, M.R., Pyle, C.J., Hernandez, R.E., Tobin, D.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
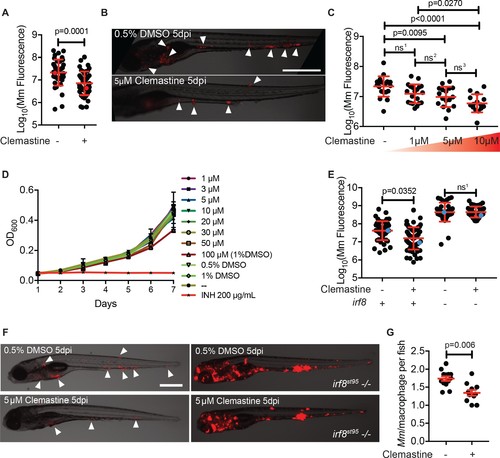
Clemastine activity is host-dependent, dose-responsive, and requires macrophages.(A) Bacterial burden per animal assessed by Mm:tdTomato fluorescence 5 days post infection (dpi) after treatment with 0.5% DMSO vehicle or 5 µM clemastine. Red dots denote the corresponding image shown in Figure 2B. Representative of five experiments. (B) Representative images from experiment in Figure 2A (red dots). Mm:tdTomato infection treated with 0.5% DMSO vehicle or 5 µM clemastine in 0.5% DMSO. White arrows denote regions of bacterial foci. Scale bar is 500 µm. (C) Quantification of Mm:tdTomato fluorescence at 5 dpi in zebrafish larvae treated with increasing concentrations of clemastine. (D) Mm:tdTomato bacterial broth culture grown in the presence of increasing concentrations of clemastine, compared to 0.5% DMSO, 1% DMSO, no vehicle (-), and 200 µg/mL isoniazid. (E) Bacterial burden of wildtype and heterozygous siblings or irf8st95 mutants, which lack macrophages, treated with 0.5% DMSO or 5 µM clemastine. Blue dots indicate animals in Figure 2F. Data are pooled from two biological replicates. (F) Representative infections from irf8st95 mutants and wildtype/heterozygous siblings from each treatment group in Figure 2E at 5 dpi. Wildtype animals (left) were equally brightened (no change in gamma settings) to show contrast of bacteria and brightfield. The irf8st95-/- example animals (right) were not brightened. (G) Number of bacteria per macrophage during treatment with 0.5% DMSO or 5 µM clemastine, 1 dpi. Each dot represents the mean number of intracellular Mm:mCerulean bacteria inside macrophages of one Tg (mfap4:tdTomato)xt11 animal at 24 hpi infected with ~ 50 CFU. Representative of three independent experiments. (A) Two-tailed, unpaired t-test. (C) Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, ns1 = 0.0864, ns2 = 0.7799, ns3 = 0.2415. Post-test for linear trend, p<0.0001. (E) Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA for unequal variances with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, ns1 > 0.9999 (A,C,E) Error bars are s.d. (G) Two-tailed unpaired t-test; error bars are s.e.m. p-Values from statistical tests on untransformed data are provided in Supplementary file 2. |
|
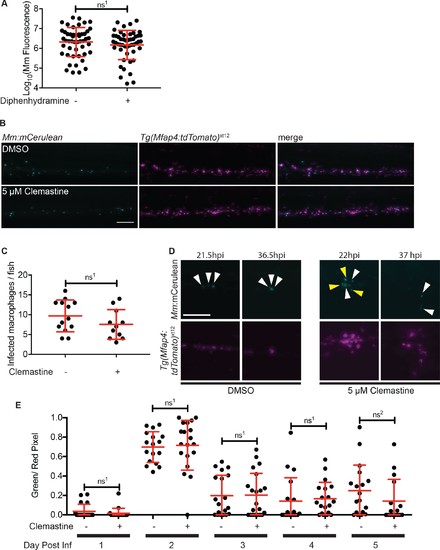
Macrophage function during clemastine treatment.(A) Bacterial burden per animal assessed by Mm:tdTomato fluorescence 5 days post-infection after treatment with 0.5% DMSO or 5 µM diphenhydramine. (B) Example images from quantification in Figure 2G. Bacteria are Mm:mCerulean and macrophages Tg(mfap4:tdTomato)xt12 are false colored in magenta, maximum intensity projection of 5 z stacks of 10 µm. Scale bar is 100 µm. (C) Number of infected macrophages per fish. Each dot represents the total number of infected macrophages in each animal from experiment in Figure 2G. (D) Stills from Video 1. Scale bar is 100 µm. Maximum intensity projection of 4 z-stacks of 15 µm. White arrows mark bacteria that are present in both initial and final timeframes, and yellow arrows mark individual bacteria that disappear during the timelapse. (E) Ratio of green to red fluorescent bacteria from Mm:aprA’::GFP,smyc::mCherry infection (~ 50 CFU) in wildtype zebrafish larvae over the course of a 5-day infection during treatment with 0.5% DMSO or 5 µM clemastine. (A) Unpaired t-test, ns1 = 0.3147, error bars are s.d. (C) Unpaired t-test, ns1 = 0.1907, error bars are s.d. (E) Unpaired t-tests between treatments for each day, ns1 > 0.9999, ns2 = 0.5505, error bars are s.d. p-Values from all transformed and untransformed data are provided in Supplementary file 3. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |
|
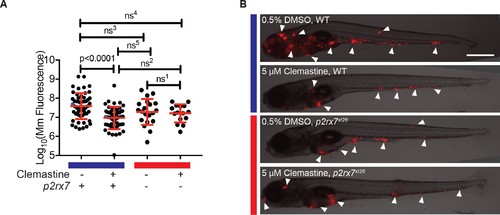
Clemastine increases frequency of macrophage calcium transients in a p2rx7-dependent manner.(A) Schematic of P2rx7 receptor, based on human structure, with CRISPR target site in exon 10 denoted with a star. (B) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated lesions in p2rx7 include a five base pair deletion (p2rx7xt26) and a two base pair deletion (p2rx7xt28) leading to a premature stop codon in exon 10. Red bar denotes p2rx7 mutants and blue bar denotes WT animals. (C) Quantification of calcium flashes observed with light-sheet microscopy in Tg(mfap4:GCaMP6F)xt25 and p2rx7xt26;Tg(mfap4:GCaMP6F)xt25 infected with ~ 50 CFU Mm:tdTomato. Each dot represents the number of flashes observed in a single infected macrophage in an animal during a 30-min time-course during treatment with 0.5% DMSO or 5 µM clemastine, 4–5 hpi, n > 3 fish for each group. All cells counted were visibly infected with Mm:tdTomato and scoring performed blind to genotype or treatment. (D) Representative calcium transient. Panels are stills from a light-sheet video in an untreated Tg(mfap4:GCaMP6F)xt25 animal infected with Mm:tdTomato. Scale bar is 25 µm. (C) Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA for unequal variances, Dunn’s multiple comparison test. ns1 > 0.9999, ns2 = 0.7007 All error bars are s.d.; p values from statistical tests on untransformed data are provided in Supplementary file 2. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Clemastine does not enhance microbicidal macrophage activities in Mm?RD1 infections. (A) Representative animals from the red dots in Figure 5A. Animals were infected with Mm:Wasabi(~50 CFU) and Mm:?RD1:Wasabi (~ 50 CFU) and treated with 0.5% DMSO or 5 ?M clemastine, 5 dpi. Scale bar is 500 ?m. (B) Bacterial burden per animal assessed by fluorescence 5 days post-infection after treatment with 0.5% DMSO or 5 ÁM clemastine. Infections were performed with Mm:tdTomato (RD1+ and cmaA2+), Tn01901:mCerulean (cmaA2-) or Mm:?RD1:Wasabi (RD1-). Each dot represents a single animal bacterial burden by fluorescence, represented as fold chance over DMSO in Figure 5?figure supplement 1C. Representative of two independent experiments. (C) Fold change in bacterial burden per experiment assessed by fluorescence of bacteria (left y-axis) or 16S rRNA qPCR (right y-axis, gray error bars). The experiment in Figure 5?figure supplement 1B is represented with green dots. Each bacterial strain is normalized to the DMSO-treated control within each bacterial strain. (D) Number of Mm:Wasabi or Mm:?RD1:Wasabi bacteria per macrophage during treatment with 0.5% DMSO or 5 ?M clemastine, 1 dpi. Each dot represents the average number of Mm:Wasabi bacteria inside the macrophages of Tg(mfap4:tdTomato)xt12 of a zebrafish larva. Representative of three experiments. (B) Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Sidak?s multiple comparison test within bacterial strains, ns1 = 0.8757. Error bars are s.d. (C) Paired t-test on left y-axis. Error bars are s.e.m. No statistics were performed on the right y-axis, represents one biological replicate performed in triplicate. (D) Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak?s multiple comparison test, ns1 = 0.4243, ns2 =0.1495. All error bars are s.e.m., p values from all transformed and untransformed data are provided in Supplementary file 3. |
|
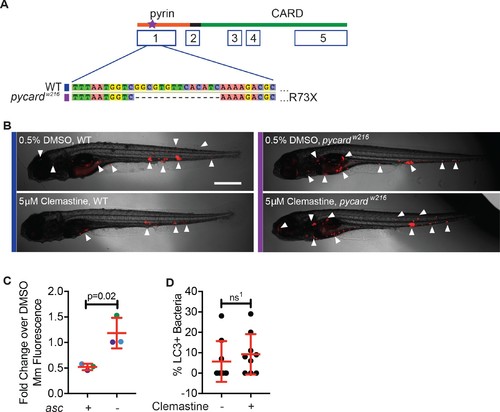
Clemastine requires inflammasome components to reduce bacterial burden.(A) TALEN-mediated lesions in pycard, the zebrafish orthologue of asc, to generate a 14 base pair deletion in exon 1, known as ascw216. (B) Representative infected animals 5 dpi from purple and blue dots in Figure 5B. Blue bar represents wildtype animals and purple bar represents ascw216 infected with Mm:tdTomato. Scale bar is 500 μm. (C) Fold change in bacterial burden per experiment assessed by fluorescence of bacteria. The experiment in Figure 5B is represented with blue dots. Each genotype is normalized to the DMSO-treated control within that genotype. (D) Percent of bacteria decorated with GFP:LC-3 puncta, 3 dpi. Each dot represents percent of bacteria with GFP:Lc-3 puncta from a single animal. Representative of two experiments. (C) Unpaired t-test, error bars are s.e.m. (D) Unpaired t-test, error bars are s.d., ns1 = 0.4585. p Values from all transformed and untransformed data are provided in Supplementary file 3. |