- Title
-
Distinct interactions of Sox5 and Sox10 in fate specification of pigment cells in medaka and zebrafish
- Authors
- Nagao, Y., Takada, H., Miyadai, M., Adachi, T., Seki, R., Kamei, Y., Hara, I., Taniguchi, Y., Naruse, K., Hibi, M., Kelsh, R.N., Hashimoto, H.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
Sox10-mediated pigment cell formation is modulated by Sox5 in zebrafish. (A, B, C, E) Swim bladder inflation stage (10 dpf). Lateral views. (C, E) UV images. (D, F) 24 dpf. Lateral views. (G, I-O) 4 dpf. (G) Dorsolateral view. (I) Lateral view. (J-O) Fluorescing xanthophores. Dorsal views anterior to the left. The sox5 mutant is indistinguishable from WT, exhibiting four stripes of melanocytes (A, B) and having fluorescing xanthophores (C, E) and gch-expressing xanthoblasts (D, F). Melanocytes are almost completely absent from sox10baz1/baz1 mutant (S8B Fig), but are partially recovered in sox10baz1/baz1 mutants that have also lost sox5 WT allele(s) (G, H). The ratio of the embryos without melanocytes or with more than one melanocytes was compared among genotypes by Chi-squared test (*p<0.05). A few xanthophores develop on surface of the head in sox10baz1/baz1 mutant (S8E, S8I and S8J Fig), and reduction of sox5 is likely to elevate xanthophore formation (K, L). Whereas sox10t3/t3 mutant almost completely lacks xanthophores (M), a few xanthophores are rescued as the sox5 WT allele(s) are reduced (N, O). The counts are shown for xanthophores on the t3 background (P). Comparison between the genotypes was performed by Kruskal-Wallis test with SDCF post hoc test. **p<0.05. A substantial number of iridophores are formed in sox10baz1/baz1 mutants (S8G and S8H Fig), and the counts are not significantly altered with reduction of the sox5 WT allele(s) (Q, p = 0.775 by Kruskal-Wallis test). Iridophores are almost completely lost in sox10t3/t3 mutant (S8I Fig), but are partially recovered in sox10t3/t3;sox5+/- and sox10t3/t3;sox5-/- mutants (R **p<0.05 by Kruskal-Wallis test with SDCF post hoc test). (H) sox10baz1/baz1;sox5+/+, n = 22; sox10baz1/baz1;sox5+/-, n = 34; sox10baz1/baz1;sox5-/-, n = 33. (Q) sox10baz1/baz1;sox5+/+, n = 46; sox10baz1/baz1;sox5+/-, n = 73; sox10baz1/baz1;sox5-/-, n = 47. (P) sox10t3/t3;sox5+/+, n = 7; sox10t3/t3;sox5+/-, n = 19; sox10t3/t3;sox5-/-, n = 16. (R) sox10t3/t3;sox5+/+, n = 24; sox10t3/t3;sox5+/-, n = 48; sox10t3/t3;sox5-/-, n = 40. (H, P-R) Bars show mean and error bar (s.d.). Arrowheads point to weakly melanised cells (G) and at the corresponding position of the head (I-O). Scale bars: (A, D) 200 ?m. |
|
Role of Sox5 in adult xanthophore development in medaka remains opposite to that in zebrafish. (A, B) Medaka. 6 mpf. (D, E) Zebrafish. 2 mpf. (D?, E?) Schematics of stripe pattern. (D?, E?) Enlarged images of X0 interstripe. (F, G) Zebrafish. 1.5 years old. In WT medaka (A), melanocytes, xanthophores (yellow arrowhead) and leucophores (white arrowhead) are scattered on the body surface. sox5-/- mutant medaka (B) have fewer xanthophores and more leucophores than WT (C, Xan and Leu, *p<0.05 by Mann-Whitney test; WT, n = 5; sox5-/-, n = 5; Bars show mean and error bar (s.d.)). Pigment cells were counted from a 1 mm2 area on the dorsal body surface. The melanocyte numbers were not significantly different between WT and sox5-/- (C, Mel, p = 0.1 by Mann-Whitney test). The adult pigment pattern of WT zebrafish is composed of 5 melanocyte stripes (2D, 1D, 1V, 2V, 3V) and xanthophore interstripes (X1D, X0, X1V, X2V) (D, D?). Zebrafish sox5-/- mutants lack two ventral interstripes (2V and 3V) (E, E?), and thus have fewer stripes than WT. This is the case regardless of sex (F, female; G, male) after the mutant fish get larger and older than 1.5 years. The sox5-/- zebrafish mutants have wider X1D and X0 (two-way arrow in D? and E?) interstripes and larger numbers of xanthophores in these interstripes than WT. (H) Scatter plot of stripe width or pigment cell numbers in each stripe, comparing sox5-/- and their WT siblings. X axis shows the standard body length of zebrafish examined. Analysis of covariance was performed to examine the differences in width or cell numbers between WT and sox5-/- mutants, by using standard length as a covariate. The p values are as follows; width X1D (p<0.05), 1D (p<0.05), X0 (p<0.05), cell number X1D (p<0.05), 1D (p = 0.985), X0 (p<0.05). The width and number of xanthophore in the xanthophore stripes (X0, X1D) in sox5-/- mutants (black boxes) show significant increase compared with WT siblings (white boxes). The number of melanocyte in the 1D stripe is comparable between WT (white boxes) and sox5-/- mutant (black boxes), but the width is slightly but significantly different (p<0.05). Scale bar: (A) 200 ?m, (D) 3 mm, (D?) 200 ?m, (F) 3 mm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
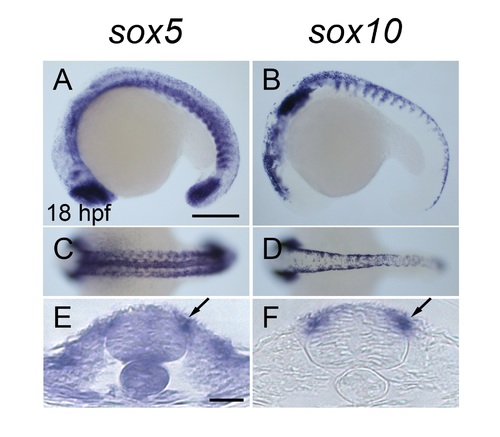
Zebrafish sox5 is expressed in premigratory neural crest similarly to sox10. (A, C, E) sox5 expression. (B, D, F) sox10 expression. (A-F) 18 hpf. (A, B) Lateral views. (C, D) Dorsal views. (E, F) Transverse sections. Strong signal of sox5 expression is detected in the head, tail bud, notochord and somites (A, C). A transverse section of the trunk region indicates that sox5 is expressed in the premigratory neural crest cells (E, arrow). (B, D, F) sox10 expression overlaps with sox5 expression in the premigratory neural crest cells (F, arrow). Scale bar: (A) 200 ?m, (E) 20 ?m. |
|
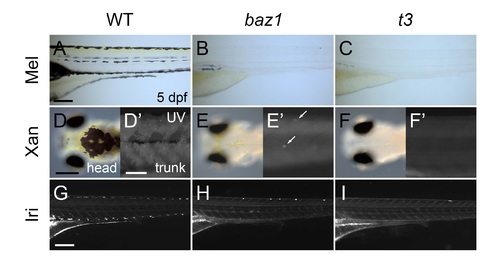
Zebrafish homozygous for the baz1 allele of sox10 show milder pigment cell phenotypes than those for t3 allele. (A, D, G) WT. (B, E, H) sox10baz1 mutant (baz1). (C, F, I) colourless/sox10t3 mutant (t3). (A-I) 5 dpf. (A-C, G-I) Lateral views of trunk. (D-F) Dorsal views. (D?-F?) UV images. Lateral views of trunk. WT zebrafish larva has four melanocyte stripes in the trunk (A). The baz1 (B) and t3 mutants (C) lack the stripes. In WT, xanthophores are widely distributed on dorsal surface of head (D). The baz1 mutant has a few xanthophores on head (E) and trunk (E?). The t3 mutant almost entirely lacks visible xanthophores (F, F?). Iridophores lie along the dorsal, ventral and yolk sac melanocyte stripes in WT (G). A few iridophores are found in the dorsal stripe and often in the lateral patches (B) in baz1 mutants (H). The t3 mutant almost completely lacks iridophores (I), but residual cells may be present in the lateral patches (C). Scale bars: (A, D, G) 200 ?m, (E?) 100 ?m. PHENOTYPE:
|