- Title
-
Involvement of Lypge in the formation of eye and pineal gland in zebrafish
- Authors
- Ji, D., Wang, S., Li, M., Zhang, S., Li, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene
|
Expression pattern of lypge. (A?C) Weak expression is observed from cleavage to gastrula stage. (D, D') Expression is detected in prechordal plate at bud stage. (E, E') Expression is tested in early pineal gland cells at about 16 hpf. (F?J') Expression is firstly examined in dorsal retina at about 25 hpf and in cone photoreceptor progenitor at about 40 hpf. (K?L) lypge is expressed in cone photoreceptor at 72 hpf and adult. A?D and E: the lateral view of embryos, D': animal pole view, E', F and G, H, I, J: dorsal view, G', H?, I? and J': disconnected single eye, K and L: sectioned eye. |
|
otx5 regulates expression of lypge. (A) Two kinds of otx5 binding sequence ?TAATC? and ?TAATT? are marked by blue and red, respectively, in promoter (? 1920 to ? 1) and downstream sequence (7601 to 11,143) of lypge. (B) Ectopic expression (arrowhead) is induced in otx5 overexpressed embryos at 24 hpf, pineal gland is indicated by arrow. (C) Left: examination of otx5 MO efficiency, expression of EGFP fluorescence in embryos at 10 hpf is absent from embryos co-injected MO-binding site + EGFP mRNA with otx5 MO. Pineal expression of lypge in wildtype and otx5 MO emryos at 24 hpf. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) |
|
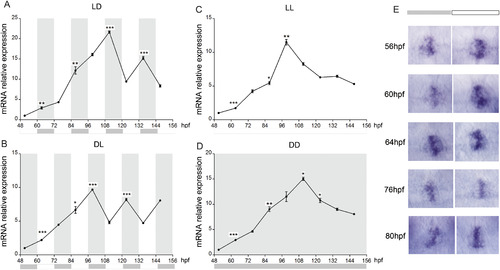
Assay for rhythmic Expression of lypge. (A?D) Expression is examined by qRT-PCR in different light-dark cycles (A: LD, B: DL, C: LL, D: DD). White and gray backgrounds represent light and dark phases. Zebrafish larvae were collected at two time points per day between 2 and 6 dpf. Embryos were sampled at zeitgeber time (ZT) 3 and 15. Statistically significant differences between the expression peak and through on each day (Fisher's t-test) are indicated:*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (E) Embryos are expose to continuous light or dark after 48 hpf and its expression in pineal gland is detected at different time. |
|
Knockdown of lypge causes small eye and small head phenotype. (A) Examination of lypge MO efficiency, left: expression of EGFP fluorescence in embryos injected MO-binding site + EGFP mRNA alone. Right: expression of EGFP fluorescence is absent from embryos co-injected MO-binding site + EGFP mRNA with lypge MO. (B) Compared with phenotype between wildtype (WT) embryos and morphants (MO) at 52 hpf. (C) Cell apoptosis assay, embryos are stained with acridine orange (AO) at 48 hpf and quantification of the number of AO positive cells in eye (green). Statistically significant differences between the WT and MO (Fisher's t-test) are indicated: ***P < 0.001. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (D) compared with phenotype in wildtype, lypge MO injected and lypge MO and p53 MO co-injected embryos at 76 hpf. (E) Apoptosis of brain cells in WT embryos and morphants. Region of pineal gland is indicated by white dotted line. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Gene, 642, Ji, D., Wang, S., Li, M., Zhang, S., Li, H., Involvement of Lypge in the formation of eye and pineal gland in zebrafish, 491-497, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene