- Title
-
Diverging roles for Lrp4 and Wnt signaling in neuromuscular synapse development during evolution
- Authors
- Remédio, L., Gribble, K.D., Lee, J.K., Kim, N., Hallock, P.T., Delestrée, N., Mentis, G.Z., Froemke, R.C., Granato, M., Burden, S.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Genes & Dev.
|
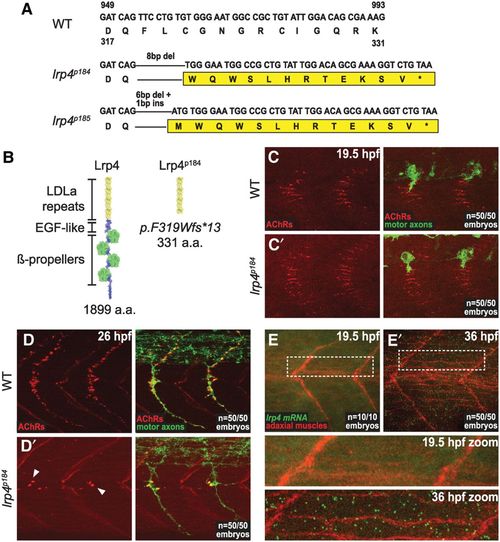
Zebrafish Lrp4 is required for synapse formation but not AChR prepatterning. (A) Sequences of wild-type zebrafish lrp4 exon 9 and sequences of lrp4p184 and lrp4p185, two frameshift alleles that were generated using TALENs targeting exon 9. (B) The protein domain structure of wild-type zebrafish Lrp4 (1899 amino acids) and the predicted structure of lrp4p184 (331 amino acids), which resembles the mouse mitt allele and is predicted to lack the β-propeller domains, the EGF-like domains, the transmembrane domain, and the intracellular region. (C,C′) Lateral views of wild-type and lrp4 mutant zebrafish embryos at the prepatterning stage (19.5 h post-fertilization [hpf]) stained for AChRs (red) and motor axons (green). Lrp4 mutant embryos show no reduction or defect in AChR prepatterning. n = 50 out of 50 embryos. (D,D′) Lateral views of wild-type and lrp4 mutant zebrafish embryos at the synapse formation stage (26 hpf) stained for AChRs (red) and motor axons (green). In contrast to the prepatterning stage, lrp4 mutant embryos show a significant reduction in AChRs clustered beneath the motor axon terminals, with only a few ?hot spot? AChR clusters remaining at the horizontal myoseptum (white arrowheads). n = 50 out of 50 embryos. (E,E′) Lateral views of in situ hybridizations performed on wild-type zebrafish embryos at the prepatterning stage (E) and synapse formation stage (E′). Lrp4 mRNA expression is undetectable at the prepatterning stage (E and zoomed panel) but robustly expressed at later stages (E′ and zoomed panel), consistent with a requirement for zebrafish Lrp4 during synapse formation but not during prepatterning. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|