- Title
-
De novo synthesis of a sunscreen compound in vertebrates
- Authors
- Osborn, A.R., Almabruk, K.H., Holzwarth, G., Asamizu, S., LaDu, J., Kean, K.M., Karplus, P.A., Tanguay, R.L., Bakalinsky, A.T., Mahmud, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife
|
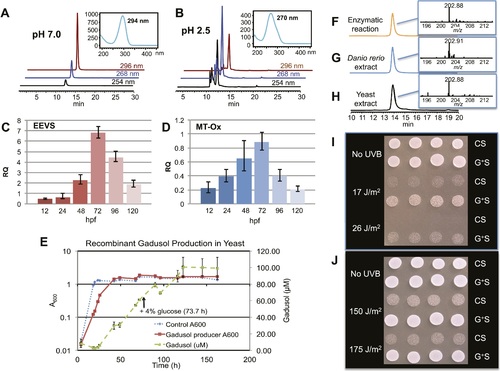
Production of gadusol in zebrafish and yeast and its sunscreen activity. (A-B) HPLC traces and UV absorptions of gadusol produced from Escherichia coli cell-free extract containing EEVS and purified MT-Ox protein at pH 7.0 and 2.5. (C-D) Transcription patterns of EEVS and MT-Ox genes during zebrafish embryonic development. qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA isolated from zebrafish embryos (n = 3) at 12, 24, 48, 72, 96, and 120 hpf. (E) Time course of gadusol production in yeast harboring the zebrafish genes. The yeast was cultured in YNB + 2% glucose supplemented with leucine and lysine at 30°C for 2 days, and growth was monitored as A600 values (control, dotted blue line; gadusol producer, solid red line). Gadusol concentration in the supernatant of 20 ml cultures (n = 3) was monitored as A296 values in 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 (dashed green line) corrected for non-gadusol background absorbance in the control supernatant, normalized to A600 value. Gadusol was quantified based on an extinction coefficient of 21,800 M-1 cm-1 in 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7. (F-H) Comparative HPLC analysis of gadusol from recombinant enzymatic reaction, zebrafish extract, and yeast extract. (I) Gadusol suppresses the UVB sensitivity of a rad1Δ yeast mutant; and (J) Gadusol increases the UVB tolerance of a wild-type (RAD1) strain. Cells suspended in control supernatant (CS) or gadusol+ supernatant (G+S) were irradiated with UVB and subsequently spotted in 3 µl aliquots (n = 4) onto YEPD plates, which were incubated at 30°C for 24 hr. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|