- Title
-
Precise and efficient genome editing in zebrafish using the CRISPR/Cas9 system
- Authors
- Irion, U., Krauss, J., Nüsslein-Volhard, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
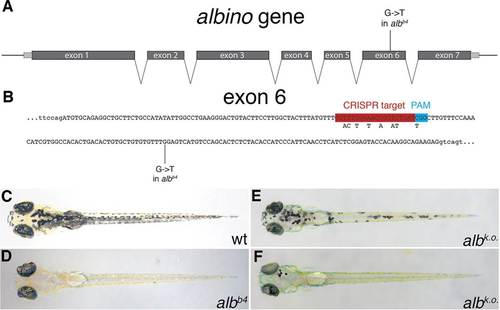
CRISPR-mediated alb knockout. (A) Schematic representation of the alb locus. The gene consists of seven exons (introns are not drawn to scale). The mutation albb4 introduces a premature stop codon into exon 6. (B) The sequence of exon 6 (in capitals). The CRISPR target site, PAM motif and the albb4 mutation are indicated; the SNPs introduced into the donor DNA fragments are shown beneath the CRISPR target site. (C-F) Dorsal views of larvae at 5dpf: uninjected control wild type (C) and albb4 (D) larvae, and injected wild-type larvae with moderate (E) and good (F) alb knockout efficiency. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
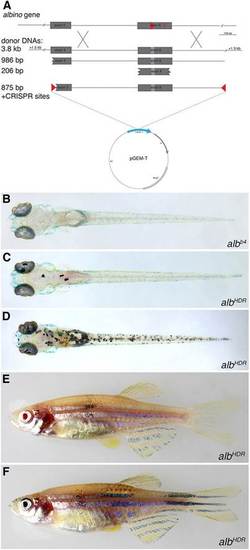
Homology-directed repair at the alb locus. (A) Donor DNAs used. The PCR fragments were also cloned into pGEM-T and injected as circular DNA molecules; the construct with the two CRISPR target sites is depicted. (B-D) Dorsal views of larvae 5dpf: uninjected albb4 control (B), low efficiency repair using linear donor DNA (C) and high efficiency repair using circular donor DNA (D). (E,F) Two examples of adult F0 fish showing pigmented melanophores as a consequence of HDR in melanophore stem cells. PHENOTYPE:
|