- Title
-
Hedgehog-PKA Signaling and gnrh3 Regulate the Development of Zebrafish gnrh3 Neurons
- Authors
- Kuo, M.W., Lou, S.W., Chung, B.C.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Co-localization gnrh3 mRNA and GFP in transgenic fish expressing GFP-LacZ under the control of the gnrh3 promoter. A?D, 3 dpf, E?H, 4 dpf. A and E, bright field (BF) view of the embryos. B and F, green color indicated gnrh3 mRNA detection by in situ hybridization. C and G, GFP immunostaining is shown as red signal. D and H, the merged pictures show co-localization of gnrh3 and GFP signals in the olfactory bulb (OB) at 3 dpf and 4 dpf. The anterior is to the left in all panels, and arrows point to the olfactory bulb. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
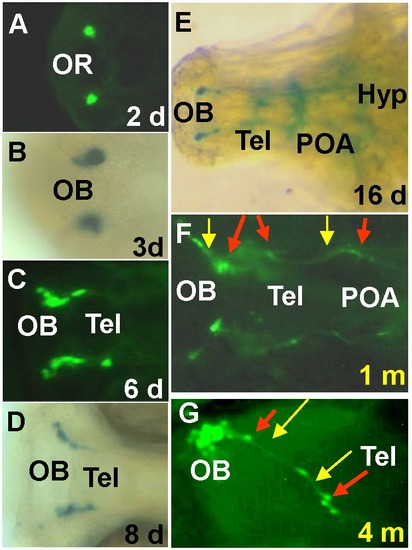
Detection of GFP- and LacZ-expressing cells in transgenic fish. A, GFP expression at the olfactory region (OR). B?D, GFP or LacZ cells in the olfactory bulb (OB) and telencephalon (Tel) at 3?8 d (days). E, lacZ cells and axons in the brain at 16 dpf. Hyp, hypothalamus. F?G, At 1 month (m) and 4 months, fluorescent axonal extensions are at OB, Tel and POA (preoptic area). Red arrows indicate cell bodies, yellow arrows indicate axons. A, C, F, G, GFP cells; B, D, E, LacZ-expressing cells. The anterior is towards the left in all panels. A, B, F, G, ventral view; C-E, dorsal view. |
|
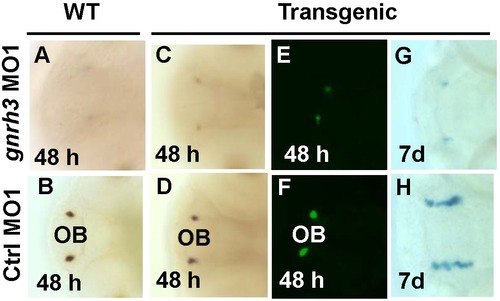
Depletion of gnrh3 expression by morpholinos causes reduction of gnrh3 cells. A?D, in situ hybridization with the gnrh3 probe. E?F, fluorescence detection of GFP cells. G?H, detection of LacZ-expressing cells. After injection of gnrh3-MO1, gnrh3 and GFP expression was reduced at 48 hpf (A, C and E) and LacZ cells in the forebrain was reduced at 7 dpf (G). B, D, F and H, Gnrh3 cells neurons after the injection of control sense MO1 (Ctrl-MO1). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
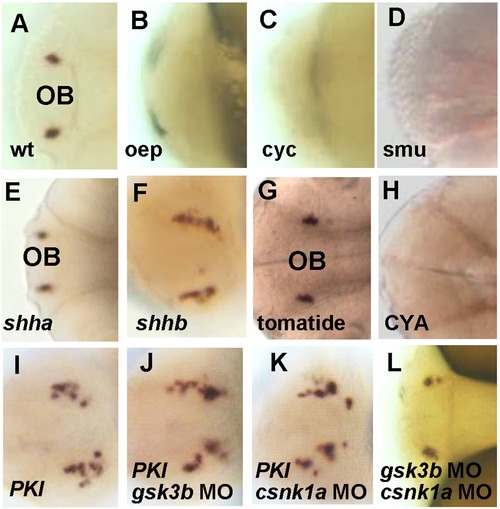
Hh-PKA pathway is required for the development of gnrh3 neurons. All embryos are at 2A?D, gnrh3 neurons were detected by in situ hybridization with the gnrh3 probe in the wildtype (wt), but not in oep, cyc and smu mutants. E?F. Ectopic GFP expression near the olfactory region in embryos injected with (F) shhb, but not (E) shha mRNA. G?H, gnrh3 signals were normal in control (G) tomatide-treated embryos, but were lost in embryos treated with (H) Hh inhibitor cyclopamine (CYA, 100 μM) at 6?10 hpf. I?K, More ectopic gnrh3-expressing cells were detected after co-injection of gsk3b-MO or cnsk1a-MO with PKI mRNA. L, Gsk3b and csnk1a double MO treatment did not increase the number of ectopic gnrh3-expressing cells. The anterior is to the left in all panels. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
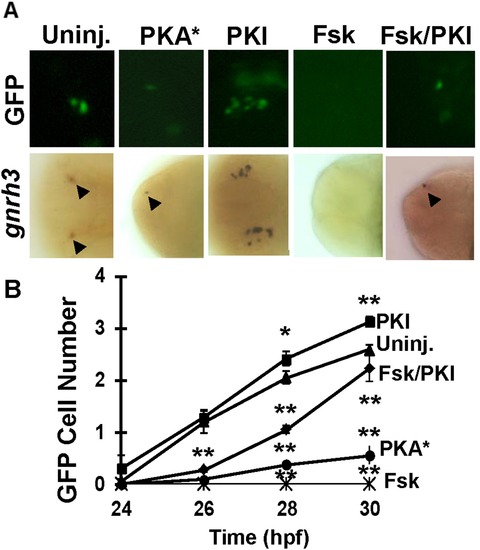
Figure 6. PKA pathway antagonizes the development of gnrh3 neurons at 30 hpf. A, GFP- (top) or gnrh3-expressing (bottom) cells in embryos injected with mRNA for constitutively active subunit of PKA (PKA*), PKI, or treated with forskolin (Fsk) or PKI + forskolin. The anterior is to the left in all panels. B, Quantitation of the numbers of GFP-expressing neurons. Twenty embryos were counted for each data point. *P<0.05. **P<0.01. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
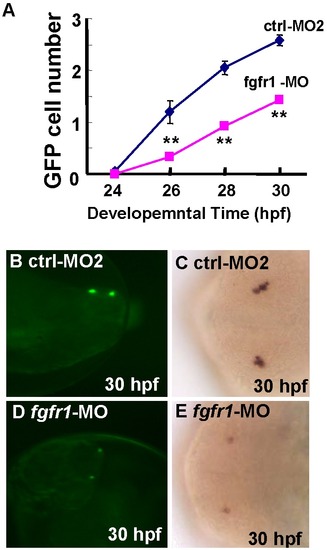
Requirement of Fgf pathway in the development of gnrh3 neurons. A, Decreased GFP cell numbers after injection of fgfr1-MO as compared with embryos injected with control MO2 (ctrl-MO2). B?E, Decreased gnrh3-expressing cells as detected by (B, D) GFP- or (C, E) in situ hybridization. The anterior is to the left in all panels. Twenty embryos were counted for each data point. **P<0.01. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
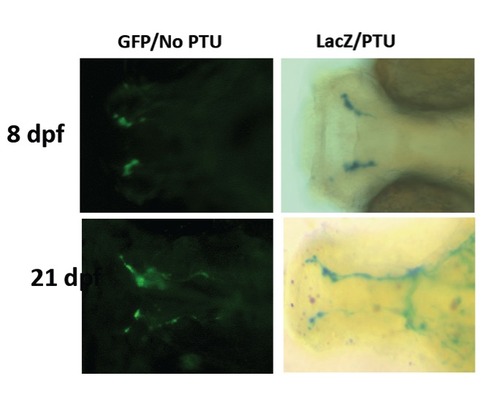
Similar patterns between LacZ staining and GFP signals at different stages. Lac Z staining are shown in zebrafish with PTU treatment. The GFP signals are expressed in zebrafish without PTU treatment. LacZ staining and GFP signals were observed at 8 dpf (upper two panels) and 21 dpf (lower two panels). |
|
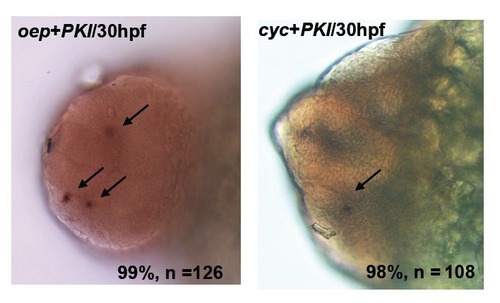
PKI rescue the gnrh3 neurons in oep or cyc mutants at 30 hpf. A, Examination of gnrh3 cell numbers in PKI-injected oep mutant. B, Examination of gnrh3 cell numbers in PKI-injected cyc mutant. |