- Title
-
Genomic organisation, embryonic expression and biochemical interactions of the zebrafish junctional adhesion molecule family of receptors
- Authors
- Powell, G.T., and Wright, G.J.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Cloning of putative jama2 and jamc2 paralogues by 3′ RACE or RT-PCR. Agarose gel electrophoresis results of amplification of full-length jama2 by 3′ RACE (A) or jamc2 by RT-PCR (B) from cDNA prepared from total RNA extracts of wild-type 24 h. p. f. zebrafish embryos. (A) Lanes: - 3′ RACE negative control; 1–4 igsf11 positive control: 3′ RACE –1 5′ primer, 2 nested 5′ primer; nested PCR –3 negative control, 4 nested 5′ primer; 5–8 jama2:3′ RACE –5 5′ primer, 6 nested 5′ primer; nested PCR –7 negative control, 8 nested 5′ primer. (B) Lanes: - negative control; + ef1α positive control; 1 jamb positive control; 2 & 4 jamc2 primers designed to amplify predicted full-length ORF; 3 & 5 jamc2 primers designed to amplify IgSF domains. M, DNA size markers with size of selected bands indicated in kbp (left). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
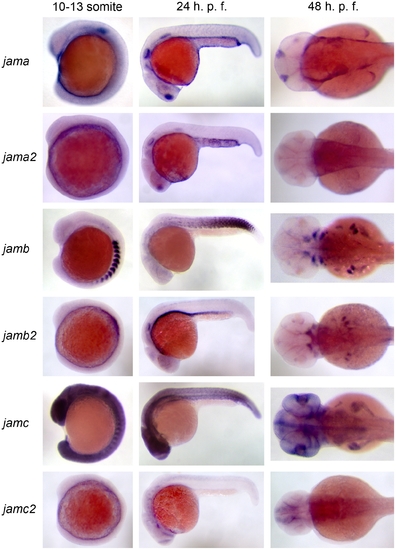
Expression patterns of zebrafish jam family genes suggest different transcriptional regulation of paralogues. Wholemount in situ hybridisation of jama (top row), jama2 (second row), jamb (third row), jamb2 (fourth row), jamc (fifth row) and jamc2 (bottom row) to wild-type embryos at three different stages of development: approximately 10–13 somites (left column), 24 h. p. f. (middle column) and 48 h. p. f. (right column). JAM-B and JAM-C orthologues show little overlap in expression during embryogenesis, suggesting different regulation of the paralogues. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements |