- Title
-
The mouse Wnt/PCP protein Vangl2 is necessary for migration of facial branchiomotor neurons, and functions independently of Dishevelled
- Authors
- Glasco, D.M., Sittaramane, V., Bryant, W., Fritzsch, B., Sawant, A., Paudyal, A., Stewart, M., Andre, P., Cadete Vilhais-Neto, G., Yang, Y., Song, M.R., Murdoch, J.N., and Chandrasekhar, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
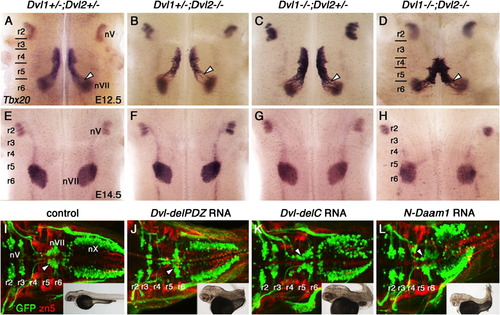
Caudal migration of FBM neurons is not affected by loss of Dishevelled function. Ventricular (A)?(D) and pial (E)?(H) views of embryos processed for Tbx20 ISH. In E12.5 control Dvl1+/-;Dvl2+/- embryos (A), FBM neurons migrate caudally from r4 into r6 (arrowhead) to form the facial motor nucleus (nVII). This caudal migration occurs normally in Dvl1+/;Dvl2-/-(B), Dvl1-/-;Dvl2+/- (C), and Dvl1-/-;Dvl2-/- mutants (D), inspite of neural tube closure defects in many of these embryos. By E14.5, FBM neurons in control embryos (E) have completed their caudal and radial migrations to form facial motor nuclei (nVII) in r6. Likewise, these nuclei are formed in r6 in Dvl-deficient embryos including Dvl1+/-;Dvl2-/- (F, 2/2 embryos), Dvl1-/-;Dvl2+/- (G, 6/6 embryos), and Dvl1-/-;Dvl2-/- mutants (H, 4/4 embryos). Neural tube defects were seen in Dvl1-/-;Dvl2-/- mutants. I-L, Dorsal views of 48 hpf Tg(isl1:gfp) zebrafish embryos processed for anti-GFP and zn5 immunohistochemistry. In control embryos (I), GFP-expressing FBM neurons migrate caudally from r4 into r6 (arrowhead) and r7 to form the facial motor nucleus (nVII). Zn5 staining labels rhombomere boundaries. The trigeminal (nV) and vagal (nX) motor neurons are located in r2 and r3, and the caudal hindbrain, respectively. Inset shows intact embryo with normal extension of the body axis. In embryos injected with Dvl-delPDZ (J), Dvl-delC (K), and N-Daam1 (L) RNA (200 pg/embryo), FBM neurons are able to migrate caudally (arrowheads) out of r4 despite convergence and extension defects resulting in a shortened body axis (insets). Positions of the nV and nX neurons are not affected by these treatments. |
|
Zebrafish Dishevelled Experiments. A, While injection of the various Dvl and Daam1 RNAs generated predicted defects in convergence and extension (CE) movements (red bars), there was no effect on the caudal migration of FBM neurons (green bars). Injection of GFP RNA did not affect CE movements or neuronal migration. Data from 2-3 experiments; number in parenthesis denotes number of embryos. B, Western blot analysis of proteins isolated from 20 hpf embryos injected with RNAs encoding various constructs. Myc-tagged proteins of the predicted sizes were detected. A Western for α-tubulin was performed simultaneously to detect tubulin as a loading control. A separate Western blot was performed to detect Flag-tagged N-Daam1. C, Dorsal views of hindbrains processed for whole-mount immunostaining with anti-GFP (green) and anti-MYC (red) antibodies. 20 hpf control uninjected embryos(left panels) and embryos injected with DvldelPDZ RNA (right panels). The mutant Dvl protein is expressed broadly throughout the hindbrain and in the FBM neurons (yellow cells, arrowheads), albeit in mosaic fashion. FBM neuron migration is not affected despite extensive expression of mutant protein both in the neurons and the surrounding tissue. The anti-MYC antibody exhibits weak non-specific labeling in control embryos (asterisks). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 369(20), Glasco, D.M., Sittaramane, V., Bryant, W., Fritzsch, B., Sawant, A., Paudyal, A., Stewart, M., Andre, P., Cadete Vilhais-Neto, G., Yang, Y., Song, M.R., Murdoch, J.N., and Chandrasekhar, A., The mouse Wnt/PCP protein Vangl2 is necessary for migration of facial branchiomotor neurons, and functions independently of Dishevelled, 211-222, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.