- Title
-
Interplay between Foxd3 and Mitf regulates cell fate plasticity in the zebrafish neural crest
- Authors
- Curran, K., Lister, J.A., Kunkel, G.R., Prendergast, A., Parichy, D.M., and Raible, D.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
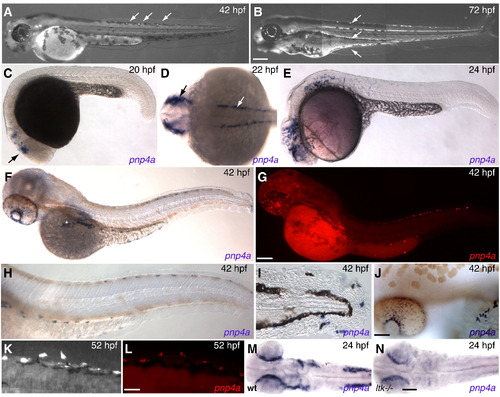
Expression pattern of iridophores and pnp4a throughout embryonic development. (A,B) Terminally differentiated iridophores illuminate under incident light. (A) At 42 hpf, three iridophores first reach terminal differentiation along dorsal stripe (arrows), iridophores scatter across the surface of retina (*). (B) By 72 hpf, iridophores more densely populate dorsal, ventral and ventral yolk stripes (arrows). Eye iridophores coalesce into a ring surrounding the lens (*). (C?J,L,M) In situ hybridization reveals pnp4a expression at different embryonic stages. (C) pnp4a first appears in anterior head region at 20 hpf, behind primordial eye (arrow). (D) By 22 hpf, pnp4a expresses exclusively in neural crest domains: lateral dorsal stripes along anterior trunk region (white arrow) and cranial region (black arrow). (E) At 24 hpf, pnp4a positive cells migrate posteriorly and ventrally. (F,H,J) Embryos treated with 1x PTU to inhibit melanin synthesis. (F) pnp4a positive cells have organized along the dorsal, ventral and ventral yolk stripes. A patch of pnp4a positive cells scatters across eye and congregates along presumptive swim bladder iridophore patch on dorsal side of yolk ball (*). (H) Close-up of trunk and tail reveal that pnp4a positive cells migrate along similar pathway as melanophores in dorsal and ventral stripes, (20x). (I) Close-up of pnp4a positive cells in tail peripheral to v-stripe of melanophores, (20x). (J) pnp4a positive cells coalesce around lens in eye and along yolk ball, (20x). (G,L) pnp4a in situ fluorescence, red: pnp4a. (K) wild-type embryo illuminated with incident light to reveal iridophore pattern then (L) fixed and processed for pnp4a fluorescent in situ hybridization. (M,N) Dorsal view of head and anterior trunk region of 24 hpf zebrafish. (M) pnp4a expression in wild-type embryo (heterozygous sibling). (N) pnp4a expression in ltk-/- (shd) mutant. Scale bars: (A,B) 300 μm; (C?G) 150 μm; (H?J) 75 μm; (K,L) 25 μm; (M,N) 80 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
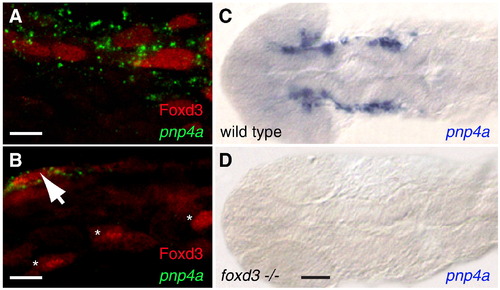
Foxd3 is necessary for pnp4a expression. (A,B) Wild-type fish co-stained with pnp4a and Foxd3, 24 hpf, anterior trunk. Green: pnp4a mRNA, red: Foxd3 antibody (A) Punctate, cytoplasmic pnp4a mRNA signal surrounds Foxd3 positive nuclei, 63×. (B) Field reveals a pnp4a+/Foxd3+ cell (arrow) adjacent to three pnp4a-/Foxd3+ cells (*), 40x. (C,D) Flat mounted head and trunk stained with pnp4a riboprobe, 22 hpf, dorsal view, anterior left, 10x. (C) wild-type (D) foxd3-/- mutant (sym1). Scale bars: (A) 10 μm; (B) 20 μm; (C,D) 70 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
foxd3/mitfa double mutant exhibits partial rescue of iridophores. (A?D) Incident light reveals iridophores on trunk and tail of 51?54 hpf zebrafish, lateral view, anterior left, 5x. (A) Wild-type zebrafish displays normal numbers of iridophores. (B) mitfa-/- (nacre) displays supernumerary iridophores. (C) foxd3-/- (sym1) displays iridophore reduction. (D) foxd3/mitfa double mutant exhibits partial rescue of iridophore phenotype as compared to foxd3-/- reduction alone. (E) Iridophores were counted along the dorsal and ventral stripes from the posterior tail region, between the cloacae and tail tip. Cell counts taken from 51 zebrafish for each genetic background: Total cell counts (wild-type: 1144), (foxd3-/-: 305), (mitfa-/-: 1615), (foxd3/mitfa double mutant: 748). Mean iridophore cell counts: (wild-type: 22.9), (foxd3-/-: 6.1), (mitfa-/-: 32.3), (foxd3/mitfa double mutant: 15.0). Bars = s.d. Scale bar: (A?D) 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
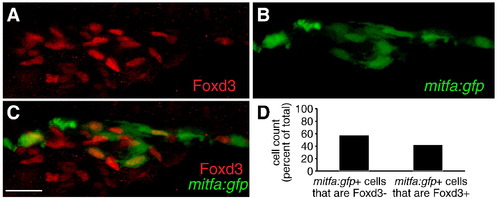
mitfa positive neural crest cells re-acquire Foxd3 expression. (A?C) Confocal images taken from lateral aspect of anterior trunk, 40x. (A) Foxd3, (B) mitfa:gfp, (C) merged: red channel: Foxd3, green channel: mitfa:gfp. (D) Cell counts of mitfa:gfp positive cells that are either Foxd3 positive or negative, counts derived from 40x confocal images at 24 hpf, numbers given as percent of total. 52% of mitfa:gfp+ cells are Foxd3- (432/748). 48% of mitfa:gfp+ cells are Foxd3+ (316/748). Scale bar = 30 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
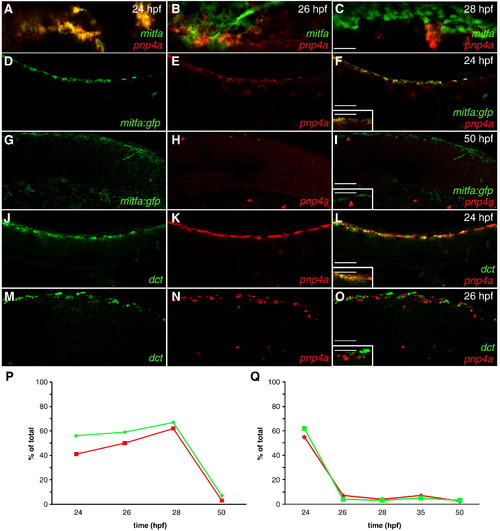
Iridoblast marker co-localizes with melanoblast markers. (A?O) Confocal images collected from lateral aspect of anterior tail region of fixed zebrafish, 20x. (A?C) Cells co-stained with mitfa riboprobe (red) and pnp4a riboprobe (green) reveal a considerable overlap at 24 hpf (A) and a diminishing overlap as development proceeds (B,C). mitfa:gfp transgenic reveals that mitfa+ cells overlap with pnp4a expression at 24 hpf (D?F) and resolve at 50 hpf (G?I). (D,G) mitfa:gfp (E,H) pnp4a. (F,I) Color merged: green: GFP expression, red: pnp4a mRNA (inset 40x). Wild-type embryos reveal that dct+ cells overlap with pnp4a expression at 24 hpf (J?L) then resolve at 26 hpf (M?O). (J,M) dct (K,N) pnp4a. (L,O) Color merged: green: dct mRNA, red: pnp4a mRNA (inset 40x). (P,Q) Percent of overlap between chromatoblast markers (see Table 1). (P) Green line = % of mitfa:gfp+ cells that are mitfa:gfp+/pnp4a+. Red line = % of pnp4a+ cells that are mitfa:gfp+/pnp4a+. (Q) Green line = % of dct+ cells that are dct+/pnp4a+. Red line - % of pnp4a+ cells that are dct+/pnp4a+. Scale bars: (A?C) 40 μm; (D?O) 60 μm; (F,I,L,O inset) 30 μm. |
|
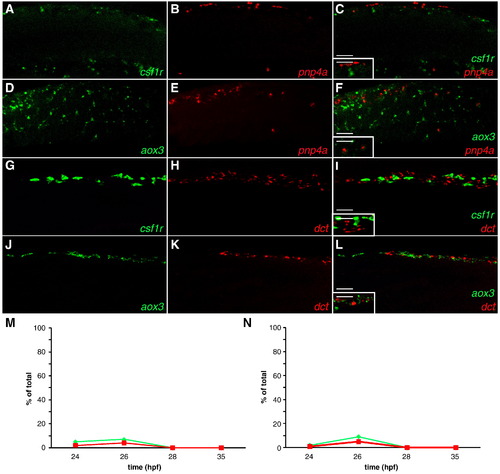
Neither iridoblast nor melanoblast markers co-localize with xanthoblast markers. (A?L) Confocal images collected from lateral aspect of anterior tail region of fixed zebrafish, 20x. (A?C,M) Wild-type embryo reveals that csf1r signal is not localized with pnp4a expression at 24 hpf (A) csf1r (B) pnp4a. (C) Color merged: green: csf1r mRNA, red: pnp4a mRNA (inset 40x). (D?F,N) Wild-type embryo reveals that aox3 signal is not localized with pnp4a expression at 24 hpf (D) aox3 (E) pnp4a. (F) Color merged: green: aox3 mRNA, red: pnp4a mRNA (inset 40x). (G?I) Wild-type embryo reveals that csf1r signal is not localized with dct expression at 24 hpf (G) csf1r (H) dct. (I) Color merged: green: csf1r mRNA, red: dct mRNA (inset 40x). (J?L) Wild-type embryo reveals that aox3 signal is not localized with dct expression at 24 hpf (J) aox3 (K) dct. (L) Color merged: green: aox3 mRNA, red: dct mRNA (inset 40x). (M,N) Percent of overlap between chromatoblast markers (see Tables 2 and 3). (M) Green line = % of csf1r+ cells that are pnp4a+/csf1r+. Red line = % of pnp4a+ cells that are pnp4a+/csf1r+. (N) Green line = % of aox3+ cells that are pnp4a+/aox3+. Red line = % of pnp4a+ cells that are pnp4a+/aox3+. Scale bars: (A?L) 60 μm; (C,F,I,L inset) 30 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
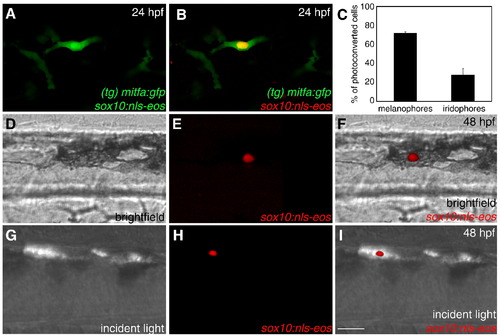
Melanoblasts and iridoblasts share a mitfa+ bi-potent precursor. (A,B) Confocal image of a double-positive sox10:nls-eos/mitfa:gfp cell surrounded by mitfa:gfp cells, lateral view, anterior trunk, 24 hpf, 40x. (A) Unconverted, pre-UV exposure. (B) Photoconverted, post-UV exposure. (C) Bar graph: 72% of identified photoconverted cells acquire a melanophore fate; 28% of identified photoconverted cells acquire an iridophore fate (n = 144) Bars = s.d. (for all values see Table 4). (D?F) Photoconverted sox10:nls-eos/mitfa:gfp cell acquires melanophore fate, lateral view, anterior trunk, 48 hpf, 40x. (D) Brightfield. (E) Red channel. (F) Merged brightfield/red channel. (G?I) Photoconverted sox10:nls-eos/mitfa:gfp cell acquires iridophore fate, lateral view, anterior trunk, 48 hpf, 40x. (G) Incident light. (H) Red channel. (I) Merged incident/red channel. Scale bars: (A,B, D?I) 30 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
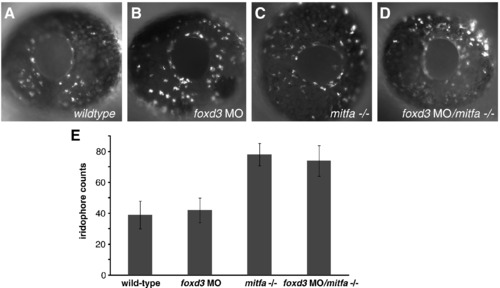
Foxd3 fails to repress eye iridophores. (A?D) Incident light reveals iridophores on eyes of 48 hpf zebrafish, lateral view, 10x. (A) Wild-type zebrafish eye displays normal numbers of eye iridophores. (B) Foxd3 morphant displays normal number of eye iridophores. (C) mitfa-/- eye displays supernumerary iridophores. (D) foxd3MO/mitfa mutant eye exhibits supernumerary iridophores. (E) Eye iridophore cell counts collected from 20 zebrafish for each genetic background. Mean iridophore cell counts: (wild-type: 39), (foxd3 MO: 42), (mitfa/-: 78), and (foxd3 MO/mitfa-/-: 74). Bars = s.d. For an internal control, trunk iridophores were counted along the dorsal and ventral stripes from the posterior tail region, between the cloacae and tail tip at 72 hpf. Mean trunk iridophore cell counts: (wild-type: 28), (foxd3 MO: 16), (mitfa-/-: 48), and (foxd3 MO/mitfa-/-: 38). Trunk iridophore standard deviation: (wild-type: ±5), (foxd3 MO: ±5), (mitfa-/-: ±4), and (foxd3 MO/mitfa-/- double mutant: ±4). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
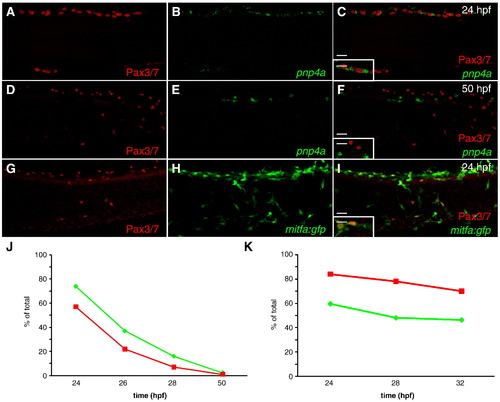
Xanthoblast marker Pax3/7 expression overlaps with iridoblast and melanoblast marker. (A?I) Confocal images collected from lateral aspect of anterior tail region of fixed zebrafish, 20x. (A?C,J) Wild-type embryo reveals that Pax3/7+ cells overlap with pnp1 expression at 24 hpf then resolve at 50 hpf (D?F). (A,D) Pax3/7 (B,E) pnp1. (C,F) Color merged: red: Pax3/7 antibody, green: pnp1 mRNA (inset 40x). (G?I) Wild-type embryo reveals Pax3/7 signal strongly localized with mitfa:gfp expression at 24 hpf (G) Pax3/7 (H) mitfa:gfp. (I) Color merged: green: mitfa:gfp, red: Pax3/7 (inset 40x). (J,K) Line graphs depicting percent of overlap between chromatoblast markers (see Table S1 in supplementary material). (J) Red line = % of Pax3/7+ cells that are pnp4a+/Pax3/7+. Green line = % of pnp4a+ cells that are pnp4a+/Pax3/7+. (K) Red line = % of Pax3/7+ cells that are mitfa:gfp+/Pax3/7+. Green line = % of mitfa:gfp+ cells that are mitfa:gfp+/Pax3/7+. Scale bars: (A?I) 20 μm; (C,F,I inset) 10 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
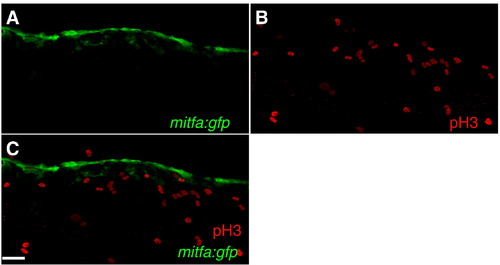
mitfa:gfp cells are post-mitotic at 24 hpf (A?C) Confocal images collected from lateral aspect of anterior tail region of 24 hpf wild-type zebrafish, anterior left, 20x. (A) mitfa:gfp (B) phosphohistone H3. (C) Color merged: green: mitfa:gfp, red: phosphohistone H3. Scale bars: (A?C) 25 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 344(1), Curran, K., Lister, J.A., Kunkel, G.R., Prendergast, A., Parichy, D.M., and Raible, D.W., Interplay between Foxd3 and Mitf regulates cell fate plasticity in the zebrafish neural crest, 107-118, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.