- Title
-
Expression of cohesin and condensin genes during zebrafish development supports a non-proliferative role for cohesin
- Authors
- Mönnich, M., Banks, S., Eccles, M., Dickinson, E., and Horsfield, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
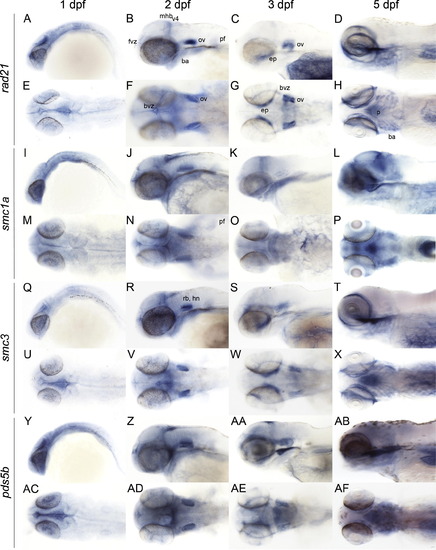
Late embryonic and larval expression (1?5 dpf) of genes encoding zebrafish cohesin subunits. Whole mount in situ hybridization of zebrafish at the indicated stages with antisense riboprobes detecting the following mRNAs: (A?H) rad21. (I?P) smc1a. (Q?X) smc3. (Y?AF) pds5b. A?D, I?L, Q?T, Y?AB: lateral views. E?H, M?P, U?X, AC?AF: dorsal views. Anterior is to the left for all. ba, branchial arches; bvz, brain ventricular zone; ep, ethmoid plate; fvz, forebrain ventricular zone; hn, hindbrain neurons; mhb, midbrain hindbrain boundary; ov, otic vesicle; p, pharynx; pf, pectoral fin; rb, rhombomeres boundaries; v4, 4th ventricle. |
|
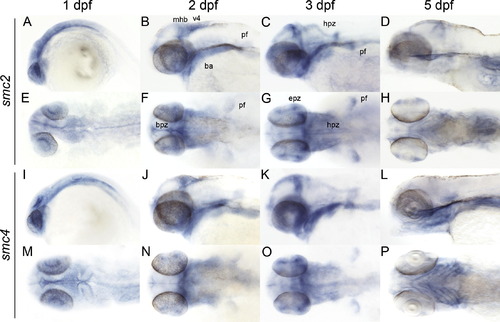
Late embryonic and larval expression (1?5 dpf) of zebrafish condensin subunits. Whole mount in situ hybridization of zebrafish at the indicated stage with antisense riboprobes smc2 (A?H), and smc4 (I?P). A?D, I?L are lateral views. E?H, M?P, are dorsal views. Anterior is to the left for all. ba, branchial arches; bvz, brain ventricular zone; epz, proliferative zone in the eye; hpz, hindbrain proliferative zone; mhb, midbrain hindbrain boundary; ov, otic vesicle; pf, pectoral fin; v4, 4th ventricle. |
|
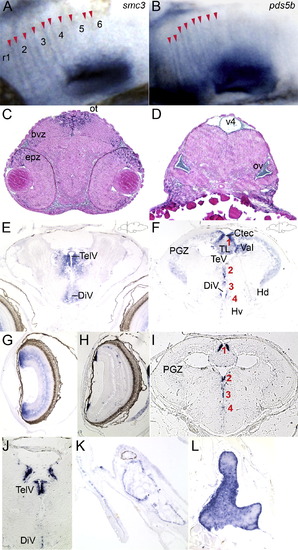
Distribution of cohesin gene expression in embryonic and 2-month-old juvenile brain. (A and B) Close-up of expression of the cohesin subunit smc3 (A) and the associated pds5b (B) at the rhombomere boundaries of 48 hpf zebrafish embryos. The labels r1?6 mark the position of the rhombomeres in (A). Red arrowheads mark the stripes of boundary cells in which the genes are expressed. (C and D) Transverse sections trough the brain of a 48 hpf embryo hybridized with a rad21 riboprobe showing regions of expression in the eye, brain and otic vesicle. (E?G) Transverse sections through brain (E and F) and eye (G) of an 8-week-old juvenile zebrafish hybridized with a rad21 riboprobe. (E) telencephalon; (F) mesencephalon. Mesencephalic proliferation zones are numbered in red 1?4: (1) tectal and torus longitudinalis proliferation zones; (2) diencephalic proliferation zones; (3) dorsal thalamic, posterior tubercular proliferation zones; and (4) hypothalamic proliferation zone. Proliferation zones were identified according to Grandel et al. (2006). (G) Transverse section though eye of 8-week-old zebrafish showing rad21 expression in cells just under the lens and throughout the retina. (H?J) Transverse sections through 8-week-old eye (H) and brain (I and J) hybridized with a pcna riboprobe. (H) Eye showing individual cells in the retina, and cells adjacent to the lens expressing pcna. (I) Mesencephalon; (J) telencephalon. Proliferation zones in (I) numbered 1?4 in red indicate the same regions of proliferation as above, expressing pcna. (K and L) Transverse sections hybridized with a rad21 riboprobe. (K) Scale next to head skeleton. (L) Thymus. bvz, brain ventricular zone; Ctec, tectal commissure; DiV, diencephalic ventricle; epz, eye proliferative zone; Hd, periventricular dorsal hypothalamus; Hv, periventricular ventral hypothalamus; ot, optic tectum; ov, otic vesicle; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; TelV, telencephalic ventricles; TeV, tectal ventricle; TL, torus longitudinalis; v4, 4th ventricle; Val, valvula cerebelli. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
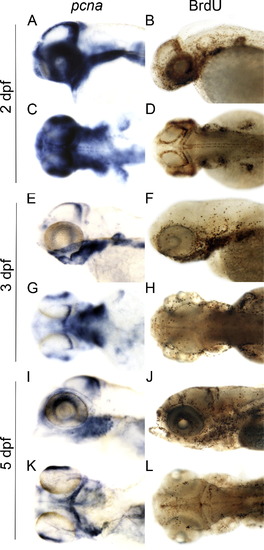
Expression of pcna and BrdU incorporation mark proliferative zones that overlap with cohesin and condensin gene expression in developing zebrafish larvae. (A, C, E, G, I and K) Whole mount larvae at the indicated days post-fertilization (dpf) hybridized with a pcna riboprobe. (B, D, F, H, J and L) BrdU labeling of developing larvae at the indicated dpf. A, B, E, F, I and J are lateral views, C, D, G, H, K and L are dorsal views. pcna expression and BrdU labeling mark many of the same cells that express cohesin and condensin genes. Anterior is to the left for all. |
|
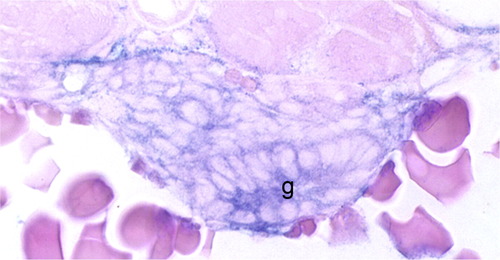
Cohesin and condensin gene expression in the gut of developing zebrafish embryos and larvae. All cohesin and condensin genes were expressed in the developing gut from 48 hpf. This example shows smc2 expression in the gut (g) of a 60 hpf zebrafish embryo hybridized with an smc2 riboprobe. |
|
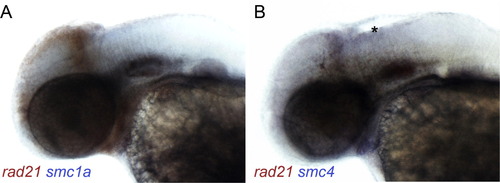
Double labeling of cohesin and condensin gene expression. Double in situ hybridizations were performed on 48 hpf embryos with a digoxygenin-labeled rad21 probe (red) and a fluorescein-labeled smc1a (A) or smc4 (B) probe (blue). (A) Expression of rad21 and smc1a appears to completely overlap. (B) Expression of rad21 and smc4 overlap to a great extent, but unique expression of smc4 is visible in the hindbrain (asterisk). |
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 9(8), Mönnich, M., Banks, S., Eccles, M., Dickinson, E., and Horsfield, J., Expression of cohesin and condensin genes during zebrafish development supports a non-proliferative role for cohesin, 586-594, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns