- Title
-
Development of a heat shock inducible gfp transgenic zebrafish line by using the zebrafish hsp27 promoter
- Authors
- Wu, Y.L., Pan, X., Mudumana, S.P., Wang, H., Kee, P.W., and Gong, Z.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene
|
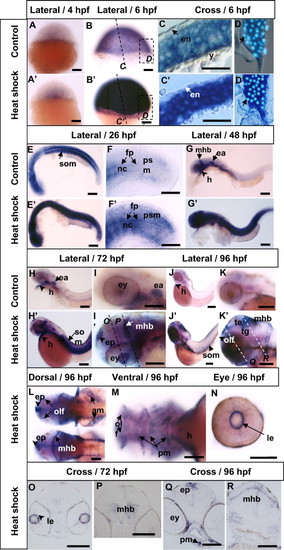
Whole-mount in situ analysis of hsp27 mRNA expression before and after heat shock. All embryos shown were hybridized with the hsp27 antisense riboprobe. (A?K) Control untreated embryos. (A′?K′) Embryos treated with heat shock at 37 °C for 1 h prior to fixation for in situ hybridization and the stages are indicated for the time fixation. (A,A′) 4 hpf embryo. (B,B′) 6 hpf embryo. (C, C′) Enlarged view of cross section of embryos shown in (B, B′). Nuclei stained with DAPI. Arrows indicate the outermost enveloping layer (en). (D,D′) Enlarged view of cross section of embryo at the blastoderm margin shown as boxed region in (B, B′) after DAPI staining. Arrows indicate the involuting cells in the margin. (E,E′,F,F′) Lateral (E, E′) and enlarged view of tail (F, F′) of 26 hpf embryos. G,G′: Lateral view of a 48 hpf embryos. (H,H′,I,I′,O,P) 72 hpf embryos; Lateral whole-mount view (H, H′), lateral view of head region (I, I′) and cross section of (I′) at the levels indicated. (J,J′,K,K′,L?N,Q,R) 96 hpf embryos: Lateral whole-mount view (J, J′), lateral view of head region (K, K′), dorsal view of the embryo in (J′) at different optical levels (L) and ventral view (M) of dissected embryo in (J′). (N) Eye of embryo shown in (J′). (Q,R) Cross sections of embryo shown in (K′) at the levels indicated. Abbreviation: am, abdominal muscles; ea; ear; en, enveloping layer; ep, epiphysis; ey, eye; fp, floor plate; h, heart; le, lens epithelium; mhb, midbrain hindbrain boundary; nc, notochord; olf, olfactory pits; pm, pharyngeal muscle; psm, presomitic mesoderm; som, somite; te, tectum; tg, tegmentum; y, yolk. Scale bar: 100 μm. |
|
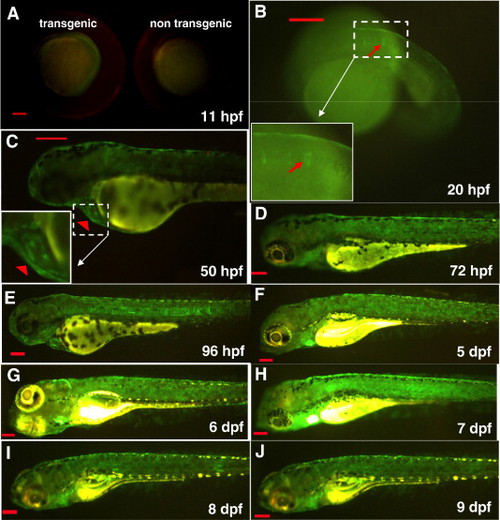
Constitutive GFP expression pattern in hsp27-gfp embryos. (A) GFP expression at 11 hpf (left) compared with the non-transgenic embryo (right). (B) GFP expression in the notochord (arrow) at 20 hpf. (C) GFP expression in the heart (arrowhead) at 50 hpf. (D?H) GFP expression at later stages from 3?9 dpf. Scale bar: 200 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
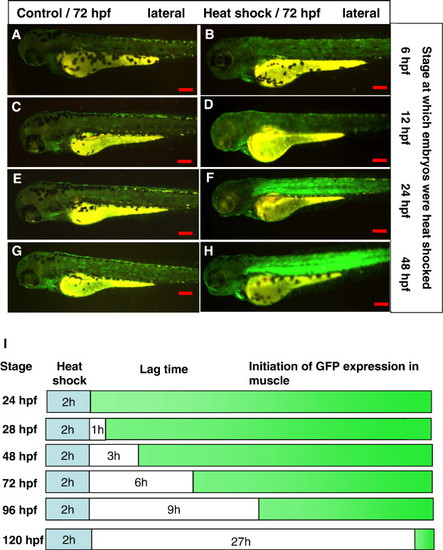
Heat shock induction of GFP expression in muscle in hsp27-gfp embryos at different stages. Hsp27-gfp embryos were heat shocked for 2 h at different stages as indicated on the right and GFP expression was observed at 72 hpf. (A,C,E,G) Control untreated embryos. (B,D,F,H) Heat shock treated embryos. No GFP expression was observed in muscles of the embryos that had been heat shocked at 6 hpf (B) and 12 hpf (D). However, strong GFP expression in muscle was observed in embryos heat shocked at 24 hpf (F) and 48 hpf (H). Scale bars, 200 μm. (I) Schematic diagram showing the interval between the end of heat shock treatment and the initiation time of muscle GFP expression. Heat shock duration, lag time and the time of GFP expression in muscle are represented by blue, white and green colors. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
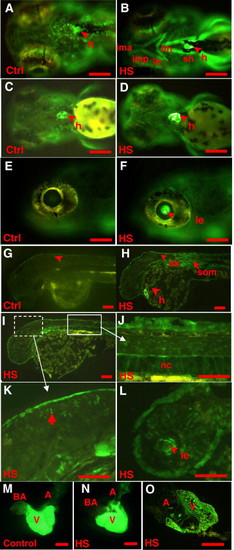
Comparison of GFP expression patterns between heat shock treated and untreated hsp27-gfp embryos. (A,C) Ventral view of 96 hpf control untreated hsp27-gfp embryos at two different focus planes. (B,D) Ventral view of 96 hpf heat shocked hsp27-gfp embryos (treated at 72 hpf) at two different focus planes. GFP was induced strongly in pharyngeal muscles (B) and heart (D) after heat shock treatment as compared to control embryos (A, C). (E,F) 8 dpf hsp27-gfp embryos with (F) or without (E) heat shock treatment at 7 dpf. Note strong induction of GFP expression in the lens (F). (G?L) Sagittal sections of 48 hpf control (G) and heat shocked hsp27-gfp embryos (H?L). Heat shock was carried at 24 hpf for 2 h and the embryos were fixed for sectioning at 48 hpf. Only very weak GFP expression was found in skin of untreated embryos (G) and heat shock induced precocious GFP expression in the heart and somatic muscle as well as stronger GFP expression in skin (H). Induced GFP was also observed in the notochord (I), central nervous system including neurons in the brain (I) and spinal cord (J), and lens (K). Panels J and K are larger magnification of the framed region from (I). (M,N) GFP expression in the adult heart with (N) or without (M) heat shock. Strong GFP expression was observed only in the ventricle of both control (M) and heat shocked fish (N). Weak expression was observed in the atrium while no expression was observed in the bulbus arteriosus. O: Section of heart from a heat shock treated hsp27-gfp fish confirming that GFP is expressed strongly in the ventricle of heart. Abbreviation: A, atrium; BA, bulbus arteriosus; h, heart; hh, hyohyoideus; ih, interhyal; ima, intermadibularis anterior; imp, intermendibularis posterior; le, lens; sh, sternohyoideus; sk, skin; som, somites; V, ventricle. The nomenclature for cranial skeletal muscles is based on Schilling and Kimmel (1997). Scale bar for A?L: 100 μm. Scale bar for M?O: 1 mm. |
|
Induction of hsp27 and hsp27-gfp expression by arsenic. (A,B) lateral (A) and ventral (B) view of 6 dpf untreated control hsp27-gfp fry. (C,D) Lateral (C) and ventral (D) view of 6 dpf fry treated with arsenic. hsp27-gfp fry were treated with 100 ppm sodium arsenate for 48 h and allowed to recover for 24 h before GFP fluorescence observation. Images of control and treated embryos were taken with the same camera exposure. (E?J) Whole-mount in situ analysis of hsp27 mRNA expression in 5 dpf fry without arsenic treatment (E, F), or treated with 50 ppm (G, H) and 200 ppm (I, J) sodium arsenate. The arsenic treatment was carried out at 72 hpf for 48 h prior to fixation for in situ hybridization. Panels E, G and I are lateral view; panels F, H and J ventral view. Abbreviation: h, heart; hh, hyohyoideus; ih, interhyal; ima, intermadibularis anterior; imp, intermendibularis posterior; mhb, midbrain hindbrain boundary; som, somite. The nomenclature for cranial skeletal muscles is based on Schilling and Kimmel (1997). Scale bar: 100 μm. |

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Gene, 408(1-2), Wu, Y.L., Pan, X., Mudumana, S.P., Wang, H., Kee, P.W., and Gong, Z., Development of a heat shock inducible gfp transgenic zebrafish line by using the zebrafish hsp27 promoter, 85-94, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene