- Title
-
Dystrobrevin and dystrophin family gene expression in zebrafish
- Authors
- Böhm, S., Jin, H., Hughes, S.M., Roberts, R.G., and Hinits, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
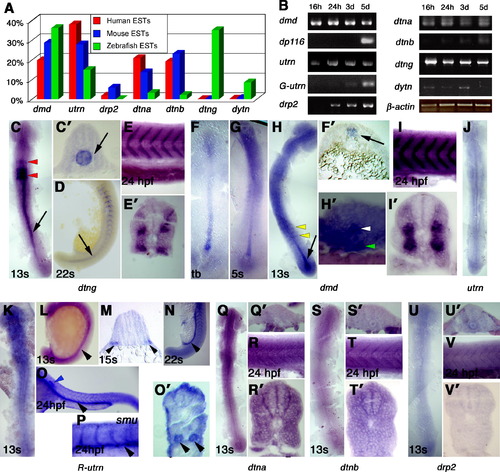
Differential expression of dystrobrevin and dystrophin genes in early stages. (A) EST frequencies of the dystrobrevin and dystrophin genes from human, mouse and zebrafish as a percentage of total dystrophin and dystrobrevin family ESTs of each species. (B) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR for mRNA samples from 16 hpf (14s), 24 hpf, 3d and 5d to the genes: dmd, dp116, utrn, G-utrn, drp2, dtna, dtnb, dtng and dytn normalized to β-actin. (C?V) In situ mRNA hybridisation for dmd (C?E), dtng (F-I), utrn (J), R-utrn (K?P), dtna (Q and R), dtnb (S and T) and drp2 (U and V) in dorsal flatmounts, anterior to top (C, F-H, J, K, Q, S, U), lateral flatmounts, anterior to left (E, I, O, P, R, T, V), lateral flatmounts, anterior to top, dorsal to right (D, L, N) or transverse sections, dorsal to top (C′, E′, F′, H′, I′, M, O′, R′, T′, V′) (C?E). Dtng mRNA is expressed strongly in the hindbrain (red arrowheads, C) and in the notochord at 13s (arrows in C and C′) but is restricted to the posterior notochord by 22s (D, arrow). At 24 hpf, no notochord expression is detected and transcripts are localised to somite borders (E and E′). F?I. Dmd is expressed strongly in the axial region at tb and 5s stage (F, F′, G). By 13s, dmd is strong in the chordo-neural hinge (arrow in H) and is expressed in the floor plate (H′, white arrowhead) and the hypochord (H′, green arrowhead). Weak dmd expression is detected in somite cells (H, yellow arrowheads). At 24 hpf, dmd transcripts are detected only in the myotome concentrated at somite borders (I,I&prime). J?O. Utrn (J) and R-utrn (K?O) are expressed in the pronephric duct from around 13s to 24 hpf (arrowheads). At 22s and 24 hpf expression is noted at muscle fibre ends at somite borders. Smo embryos lacking slow cells have similar expression in muscle and pronephric duct (P). Note the expression in the lateral line primordia (blue arrowhead). (Q and R) At 13s, dtna mRNA shows a diffuse widespread signal (Q and Q′). No specific expression is detected at 24 hpf in the somite area (R and R′). (S-V) Little specific dtnb expression (S and S′) or drp2 (U and U′) was found at 13s and at the somitic area at 24 hpf (dtnb: T and T&prime& drp2: V and V′). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
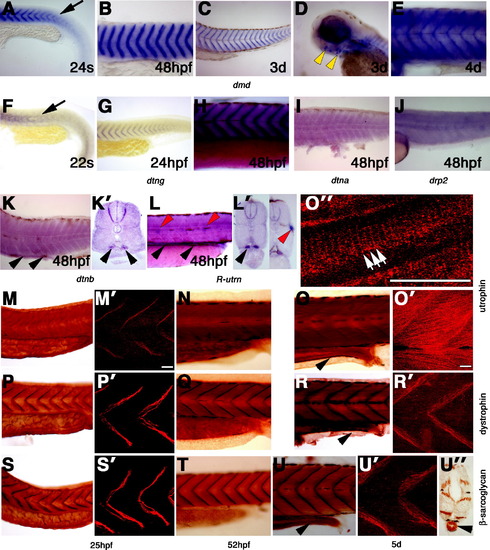
Expression of dystrobrevin and dystrophin genes in muscle, kidney and gut development. (A?L) In situ mRNA hybridisation for dmd (A?E), dtng (F?H), dtna (I), drp2 (J), dtnb (K and K′), R-utrn (L and L′) in lateral flatmounts, anterior to left (A?L), or transverse sections, dorsal to top (K′, L′). (A?H) Expression of dmd and dtng mRNA in muscle begins to accumulate at ends of recently differentiated fibres (arrows in A and F) at the somite borders from 22s, and persists at that location until after hatching (B, C, E, G, H). By 3d, some head muscles express dmd (yellow arrowheads, D). (I?K) At 48 hpf, low mRNA levels of dtna, dtnb and drp2 are detected in muscle fibres in somites, but dtnb is also present in the pronephric duct (K and K′, arrowheads). (L) At 48 hpf, R-utrn mRNA is expressed strongly in the pronephric duct (black arrowheads) and in the lateral line neuromasts (red arrowheads, L and L′-right panel) and is diffuse in muscle. (M?U) Wholemount immunohistochemistry for utrophin (M?O), dystrophin (P?R) and β-sarcoglycan (S?U) in lateral flatmounts, anterior to left, in either diaminobenzidine staining (M?O), confocal stacks of one side of somites 12?14 (M′, O′, P′, R′, S′, U′), a single confocal scan (O″), or transverse section, dorsal to top (U′). By 25 hpf dystrophin (P, P′) and β-sarcoglycan (S, S&prime) proteins are detected in muscle fibres concentrated at fibre ends, whereas utrophin protein is more evenly spread in muscle fibres. After 48 hpf, utrophin protein (N?O′) labels fibres uniformly. Note the costameric expression of utrophin in slow fibres (white arrows, O″). Between 48 hpf and 5d, dystrophin (Q?R′) and β-sarcoglycan (T?U′) proteins are spread in muscle fibres, but remain concentrated mainly at fibres ends. Note the immunoreaction in the gut at 5d with all three proteins (arrowheads in O, R, U, U′). All bars 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
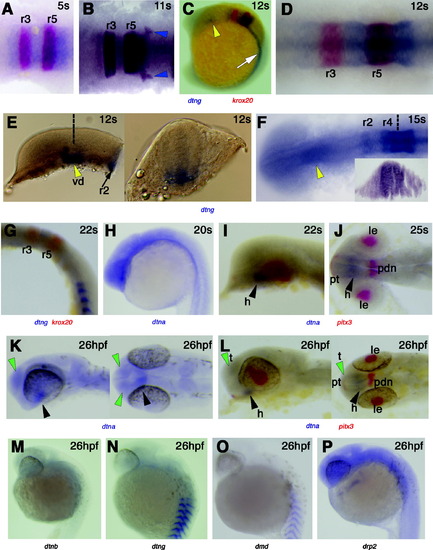
Expression of dystrobrevin and dystrophin genes in head development. In situ mRNA hybridisation in dorsal flatmounts, anterior to left (A, B, D, F, J, K-right panel and L-right panel), wholemounts in lateral view, anterior to top (C, G, H, M?P) or to left (E-left panel, I, K and L-left panel), and transverse sections, dorsal to top (E-right panel, F-inset). (A?G) Dtng mRNA is expressed in r2 and r4?6 from 5s?15s whereas krox20 (red) is expressed in r3 and r5 (A?D, F). Expression is throughout the dorso-ventral axis of the rhombomere (F, inset), including neural crest precursors within and as they are leaving the neural tube (B, blue arrowheads at r6). By 22s, expression of dtng has declined in rhombomeres leaving the highest signal in r4 and away from rhombomere borders (G), and is lost by 26 hpf (N). Expression is also detected in the diencephalon between 5?15s concentrated at the left side (C, E, F, yellow arrowheads). Transverse section at the level of the dotted line (E) shows that expression is ventral and stronger at the midline and left of it. (H?L) Low level of dtna mRNA expression is detected throughout the brain with stronger expression in the hypothalamus from 20s to at least 26 hpf (black arrowheads) whereas pitx3 (red) stains the lens, posterior diencephalon and pituitary. Note dtna expression in the telencephalon at 26 hpf (green arrowheads). (M?P) Drp2 (M) is widely expressed in the developing brain at 26 hpf, whereas little dtnb, dtng and dmd brain expression is detected. r, rhombomere; vd, ventral diencephalon; h, hypothalamus; t, telencephalon; le, lens; pdn, posterior diencephalon; pt, pituitary. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 8(2), Böhm, S., Jin, H., Hughes, S.M., Roberts, R.G., and Hinits, Y., Dystrobrevin and dystrophin family gene expression in zebrafish, 71-78, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns