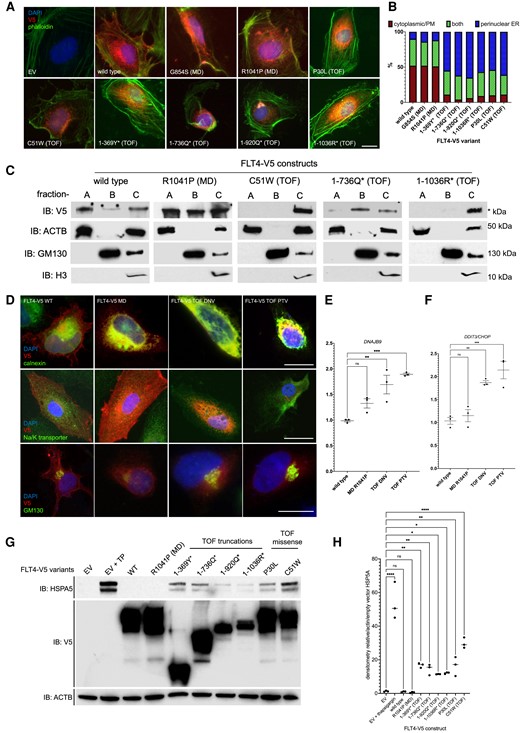
Fig. 2 Subcellular localization and proteostatic signalling consequences of FLT4 TOF variants. (A) HUVECs expressing WT, MD, and TOF FLT4-V5 variants, stained with anti-V5 (red, FLT4), phalloidin (green, actin filaments), and DAPI (blue, nuclear stain). Scale bar, 10 ?m. (B) Cells scored for three types of V5 staining, perinuclear/ER, PM/cytoplasmic, or both. One hundred cells in each group scored in each of three biological repeats. (C) Subcellular fractionation followed by immunoblotting for COS7 cells expressing FLT4 WT, MD, TOF-DNV, or two TOF-PTV variants. Fractions: A?PM, cytoplasmic; B?vesicular/Golgi apparatus-associated; or C?nuclear/perinuclear, ER. Markers: ACTB, cytoplasmic or nucleoplasmic cytoskeletal; GM130, Golgi apparatus; H3, histone 3, nuclear marker. V5-C-terminally tagged FLT4 variants. (D) Colocalization of FLT4-V5 tagged proteins with markers of the ER: calnexin; PM, Na/K-transporter; GM130, Golgi apparatus. (E and F) The activation of gene expression of proteostatic signalling by FLT4-TOF-DNV and FLT4-TOF-PTV variants. n = 3; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (G) Activation of proteostatic signalling in HEK293T cells measured through HSP5A protein expression assessed by immunoblot. (H) Densiometric analysis of HSP5A bands relative to actin/EV from (C). n = 3, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA compared with EV.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Cardiovasc. Res.