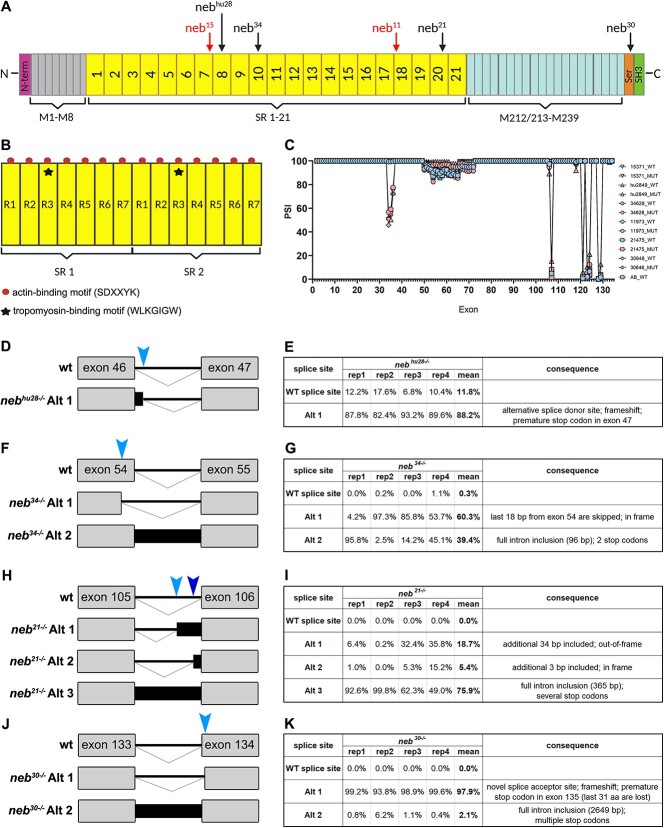
Figure 1
Zebrafish nebulin structure and nebulin mutations. (A) Diagram of zebrafish nebulin with position of mutations. N-terminus of nebulin consists of a glutamic acid rich sequence followed by several distinctive domains that mediate interactions with tropomodulin. Central region of nebulin has a repetitive, modular structure, and, in zebrafish, is organized into 21 super-repeats (SR). The C-terminus of nebulin consists of several linker modules, a serine-rich and an SH3 domains, which mediate interactions with proteins in the Z-disk. (B) Diagram of two SR. Each SR is made up of seven simple repeats (R1-R7) and contains a conserved WLKGIGW motif (troponin/tropomyosin binding site) in R3 (star). Each simple repeat contains an actin-binding motif (SDXXYK) (dots). (C) Percent spliced in index (PSI) showing alternative splicing in nebulin. Skipping of exons 33–37 was observed only in