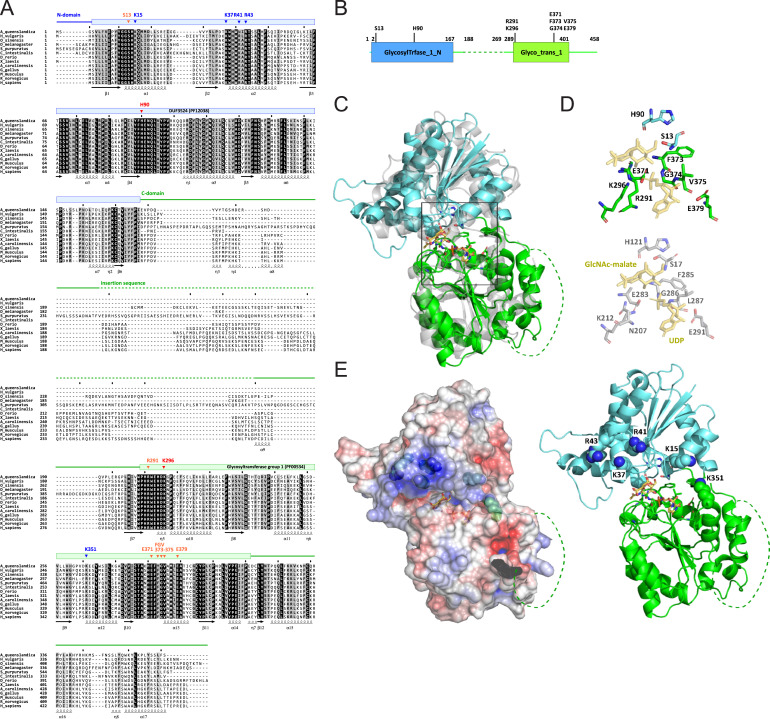
Fig. S11 Sequence alignment and structural characterization of human QTMAN, related to Figure 3 (A) Multiple alignment of 13 QTMAN orthologs by MAFFT [S1]. Conserved domains are shown by colored bars and lines above the alignment. Secondary structures defined from a predicted structure of human QTMAN are indicated below the alignment. Residues predicted to be essential for enzymatic activity of QTMAN are indicated by arrowheads: red, catalytic residues; orange, conserved residues of the catalytic center; blue, basic residues that may recognize the substrate tRNA. (B) Schematic diagram of the domains of human QTMAN. Color coding is coordinated with (A). Conserved residues involved in catalytic activity or tRNA recognition (shown in A) are indicated. (C) Overall structure of human QTMAN predicted by AlphaFold (https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q4AE62 ) superimposed on GshA (gray, 5d00 chain B). The N-terminal domain (NTD) and C-terminal domain (CTD) are colored cyan and green, respectively. The catalytic center located in the cleft of NTD and CTD is boxed. The insertion sequence (shown in A) is shown as a dotted line. (D) Catalytic center of QTMAN (upper) and GshA (lower) with UDP and GlcNAc-malate as a post-glycosyl transfer state. (E) (Left) Electrostatic surface potential generated by eF-surf (https://pdbj.org/eF-surf/top.do ) [S2] overlayed on a cartoon model of the QTMAN structure. Positively and negatively charged areas are colored blue and red, respectively. (Right) Conserved positively charged residues (shown in A) are labeled and shown as ball-and-stick models.
Reprinted from Cell, 186(25), Zhao, X., Ma, D., Ishiguro, K., Saito, H., Akichika, S., Matsuzawa, I., Mito, M., Irie, T., Ishibashi, K., Wakabayashi, K., Sakaguchi, Y., Yokoyama, T., Mishima, Y., Shirouzu, M., Iwasaki, S., Suzuki, T., Suzuki, T., Glycosylated queuosines in tRNAs optimize translational rate and post-embryonic growth, 5517-5535.e24, Copyright (2023) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell