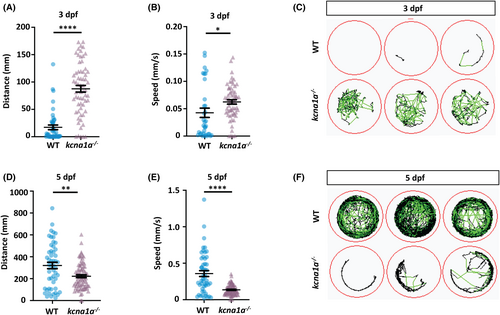
Fig. 2 Spontaneous behavior analysis of kcna1a−/− zebrafish. (A) Quantification of distance traveled at 3 dpf tracked in 100% light for 30 min. kcna1a−/− move higher distances compared to WT. WT, n = 44; kcna1a−/−, n = 63. (B) Quantification of speed at 3 dpf tracked in 100% light for 30 min. Speed of kcna1a−/− is significantly higher than WT. WT, n = 34; kcna1a−/−, n = 60. (C) Locomotor plots at 3 dpf, showing that kcna1a−/− are more active than WTs. WT, n = 20; kcna1a−/−, n = 20. (D) Quantification of distance traveled at 5 dpf tracked in 100% light for 30 min. Distance traveled by kcna1a−/− is significantly reduced compared to WT. WT, n = 51; kcna1a−/−, n = 84. (E) Quantification of speed at 5 dpf tracked in 100% light for 30 min. Speed of kcna1a−/− is significantly reduced compared to WT. WT, n = 50; kcna1a−/−, n = 84. (F) Locomotor plots at 5 dpf, showing that kcna1a−/− are moving less and have abnormal swimming patterns. WT, n = 20; kcna1a−/−, n = 24. Data are mean ± SEM, *p ≤ .05, **p ≤ .01, ****p ≤ .0001- Unpaired t test
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Epilepsia