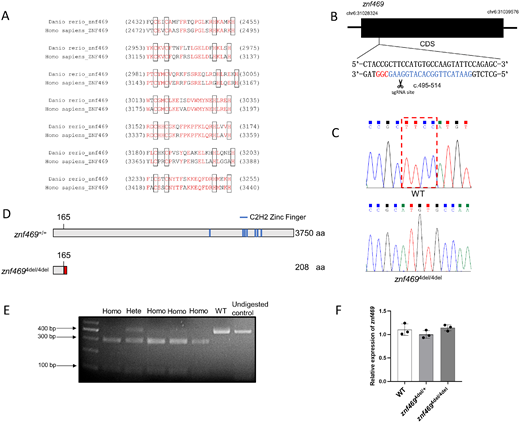
Fig. 2 Generation of znf469 mutant zebrafish. (A) Sequence alignment of the seven C2H2 zinc finger protein domains in zebrafish Znf469 protein and human ZNF469 protein. The identical residues are colored in red. Residues shown in the black box are the paired cysteines and histidines, which bind the zinc ion. (B) Schematic diagram of the zebrafish znf469 gene CDS region. The single-guide RNA (sgRNA) targeting site is marked in blue, and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence CGG is marked in red. (C) Sanger sequencing results revealed a 4-bp deletion (c.496-499del) in the znf469 homozygous mutant zebrafish. (D) Schematic representation of the protein structure of Znf469 and the position of the seven predicted C2H2 zinc finger domains. The 4-bp deletion caused a frameshift; the 166th and subsequent amino acids began to change (marked with red segment) and then generated a premature stop codon, leading to early termination of protein translation and a truncated Znf469 protein with 208 amino acids in znf4694del/4del zebrafish. (E) The mutant zebrafish were genotyped with PCR, followed by NspI digestion. The undigested WT PCR product was loaded as a control. The mutant allele could be digested into two fragments for the addition of the NspI digestion site, but the WT allele could not be digested. (F) qRT-PCR analysis revealed no significant difference in the level of znf469 mRNA in the WT, znf4694del/+, and znf4694del/4del larvae at 7 dpf. Three biological replicates were performed, and the data are shown as the mean ± SD.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.