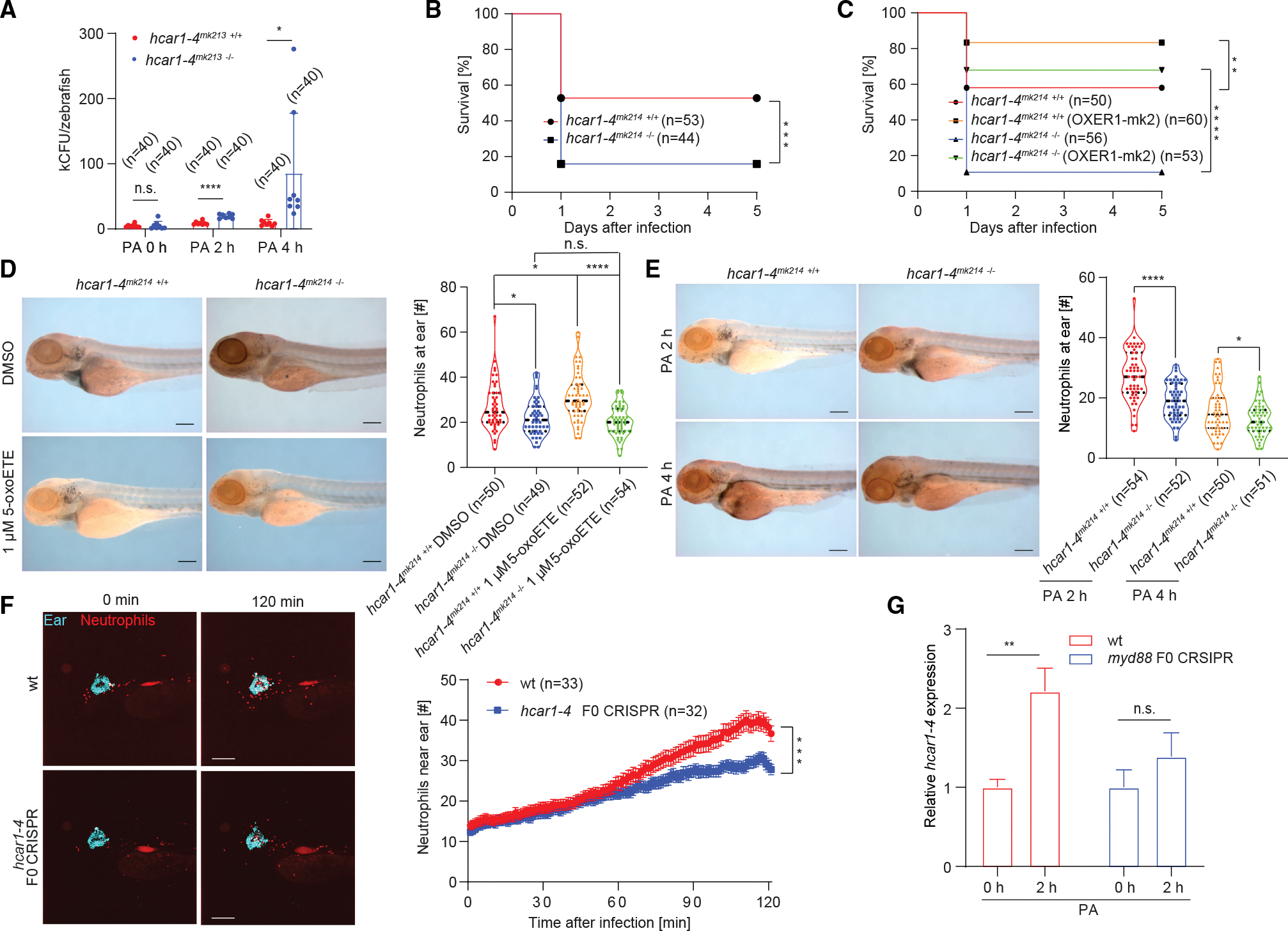
Fig. 2
(A) Colony forming units (CFU) per infected larvae at indicated times after infection. *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.00001; Student?s t test (two tailed, two sample unequal variance test). Error bars, SD of eight independently infected zebrafish pools (five larvae per group) comprising a total of n = 40 larvae per pool.
(B and C) Meier-Kaplan survival plots of PA-infected hcar1?4mk214 +/+ (WT) and hcar1?4mk214 ?/? larvae without (B) or with (C) ectopic expression of human OXER1 fused with mKate2 (OXER1-mk2). **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; log rank test. Parentheses, number of injected larvae per group.
(D) 5-oxoETE-dependent neutrophil recruitment to infected ears requires hcar1?4. Larvae were injected with PA mixed with pure 5-oxoETE (in DMSO) or DMSO alone as vehicle control. During infection and incubation, the larvae were kept under isotonic bathing conditions (Iso E3) to suppress osmotic tissue damage signals as previously described in Huang and Niethammer, 2018.24 Left panel, representative images of Sudan-black-stained neutrophils at the infected ears of WT and hcar1?4mk214 ?/? larvae 2 h after ear injection. Scale bar, 200 ?m. Right panel, quantification of neutrophil counts at the ears at the indicated times after infection. Violin plots lines denote first quartiles (top line), medians (middle line), third quartiles (bottom line). Violin plot points denote neutrophil counts in individual larvae. *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001; n.s., p > 0.05; Student?s t test (two tailed, two sample unequal variance test). N, total number of injected larvae per condition.
(E) Left panel: representative images of Sudan-black-staining of neutrophils at the infected ears of WT and hcar1?4mk214 ?/? larvae. Scale bar, 200 ?m. Right panel: quantification of neutrophil recruitment to the ears at the indicated times after infection. Violin plots lines denote first quartiles (top line), medians (middle line), and third quartiles (bottom line). Violin plot points denote neutrophil counts in individual larvae. *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001; Student?s t test (two tailed, two sample unequal variance test). Parentheses, total number of injected larvae.
(F) Live imaging of neutrophil recruitment to ear in WT and hcar1?4 F0 CRISPR larvae (TG(lyz:pm2-mk2) background). Left panel: representative time-lapse images at indicated times after infection. Cyan, fluorescent beads co-injected with PA into the ear. Red, mKate2-expressing neutrophils. Scale bar, 200 ?m. Right panel: neutrophil number in a 390 ?m × 390 ?m × 100 ?m box around the ear counted by 3D segmentation of confocal imaging stacks. Error bar, SEM of n infected WT (red) or F0 CRSIPR (blue) larvae. ***p < 0.001; Student?s t test (two tailed, two sample unequal variance test) applied to the final time point (t = 120 min).
(G) Relative mRNA expression levels of hcar1?4 at 2 h after PA ear infection as measured by qRT-PCR in 3 dpf zebrafish larvae (WT and myd88 F0 CRISPR). Actin was used as an internal control. Error bars, SD of three different pools of zebrafish larvae. **p < 0.01; n.s., p > 0.05; Student?s t test (two tailed, two sample unequal variance test).
See also Figures S2 and S3.