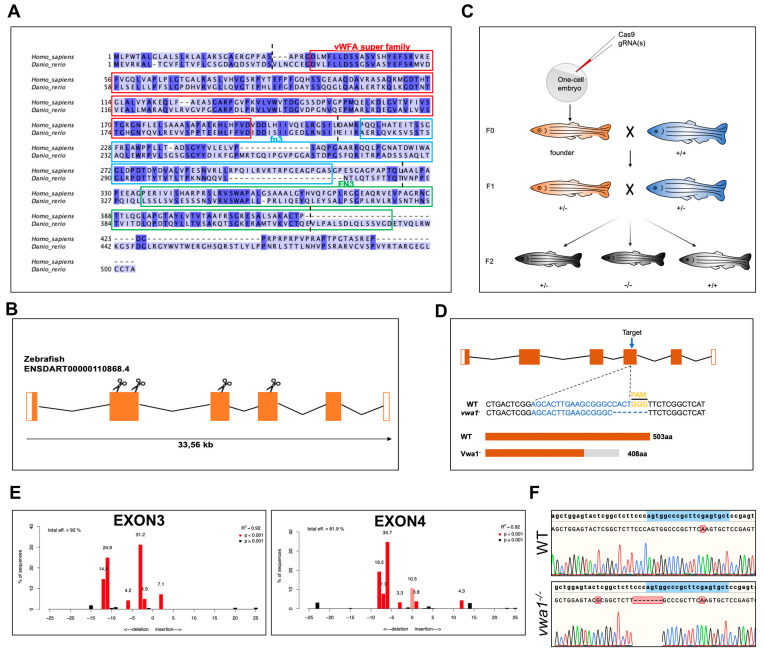
Figure 1
Conservation of vwa1 across species and generation of vwa1 knockout zebrafish by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of amino acids for human (445 aa) and zebrafish (503 aa) VWA1. Identical amino acids are shaded blue. The von Willebrand factor A-domain (vWFA), first fibronectin type III repeat domain (fn3), and second fibronectin type III repeat domain (FN3) are marked with red, blue, and green boxes, respectively. The boundaries between exons are marked with black dashed lines. (B) Structure of exons and introns of zebrafish vwa1. Untranslated regions are represented by white boxes, and coding regions are represented by orange boxes. Scissors indicate the position of the four CRISPR guides used to generate vwa1-KO crispants. (C) Stepwise construction of mutants. Adult F0 zebrafish were outcrossed with WT zebrafish, and their offspring were genotyped by PCR and Sanger sequencing to identify germline transmission of the vwa1 deletion (F0 founders). A selected F0 founder was then crossed with WT zebrafish to obtain F1 heterozygotes, which were inbred to obtain F2 homozygous mutants. (D) Detailed illustration of mutant line generated by targeting exon 4. (E) Validation of the efficiency of gRNAs. Validation of the second gRNA targeting exon 2 failed owing to its intron-adjacent location. (F) Schematic diagram and sequencing results for WT controls and the vwa1 mutant line in the F2 generation generated by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Lower panel shows the target sequence (blue), protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence (yellow), and 7-bp deletion in the mutant line.