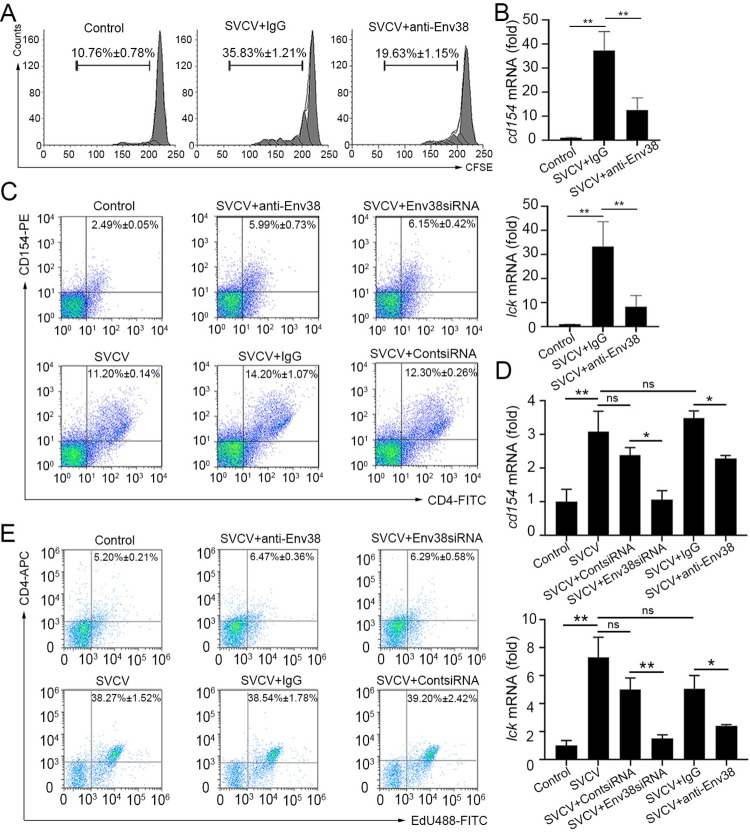
Fig 7
(A and B) In vitro examination on the proliferation (A) and activation (B) of CD4+ TSVCV cells isolated from zebrafish stimulated with inactivated SVCV (106 TCID50) and impaired by blockade of Env38 on APCs with anti-Env38 Ab (5 μg/ml) as determined by the CFSE dilution through FCM analysis and the transcriptional expression of cd154 and lck genes through RT-qPCR. (C and D) In vivo examination on the activation of CD4+ T cells stimulated with SVCV (105 TCID50) and impaired by blockade or knockdown of Env38 with i.p administering anti-Env38 Ab (10 μg/fish) or Env38siRNA-LV (1×106 TU/fish) as determined by the percentage of CD4+CD154+ T cells with mouse anti-CD154 (1:500) and rabbit anti-CD4 (1:500) in leukocytes from spleen, head kidney and peripheral blood through FCM analysis (C) and the transcriptional expression of cd154 and lck genes through RT-qPCR (D). (E) In vivo examination on the proliferation of CD4+ T cells of zebrafish stimulated with SVCV (105 TCID50) and impaired by blockade or knockdown of Env38 with i.p administering anti-Env38 Ab (10 μg/fish) or Env38siRNA-LV (1×106 TU/fish) as determined by the percentage of CD4+EdU+ T cells with rabbit anti-CD4 (1:500) in leukocytes from spleen, head kidney and peripheral blood as determined by FCM analysis. Nonrelated control groups were administered with isotype IgG or scrambled siRNA-LV. Negative control groups received mock PBS. The data presented in each block diagram indicated the average percentage of CD4+CD154+ T cells or CD4+EdU+ T cells in each treatment group. RT-qPCRs were run in combination with the endogenous β-actin control. Error bars represented SEM. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns, no significant difference).