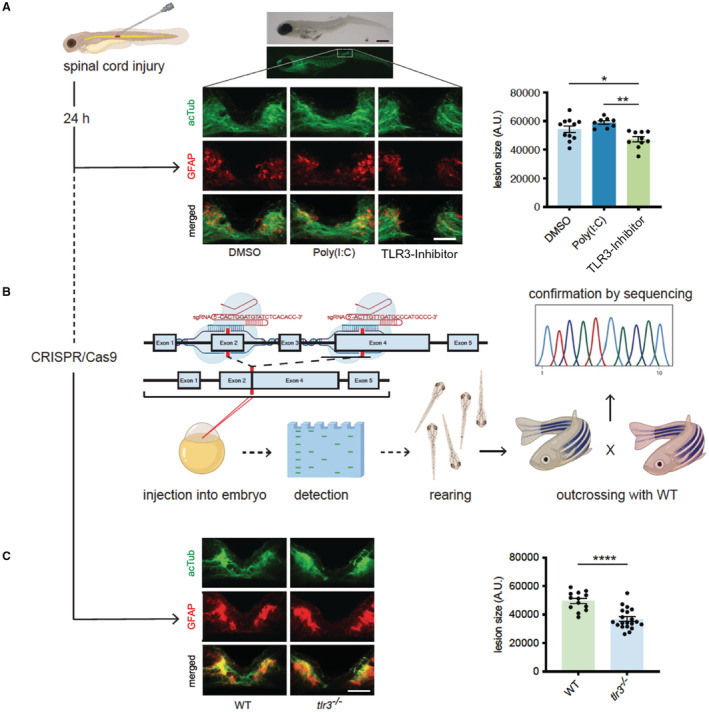
Fig. 2
A, Zebrafish larvae (4dpf) underwent traumatic spinal cord injury. After 24 hours, regeneration of spinal cord was assessed via immunofluorescence staining of acetylated Tubulin and glial fibrillary acidic protein. Inhibition of tlr3 prevents neuronal regeneration in zebrafish upon spinal cord injury. Scale bar: 500 μm (top); 50 μm (bottom). Data are means±SEM. *P<0.05; **P<0.01. n=11 (DMSO), n=8 (Poly(I:C)), n=10 (TLR3‐Inhibitor). B, TLR3‐deficient zebrafish were generated as illustrated using CRISPR/Cas9. C, Zebrafish lacking tlr3 failed neuronal regeneration upon spinal cord injury. Data are means±SEM. ****P<0.0001 n=13 (wild‐type), n=20(tlr3 −/−). Statistical comparisons between multiple groups: 1‐way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis (A). Statistical comparisons between 2 groups: Student t‐test (B). acTUB, acetylated Tubulin; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; TLR3, Toll‐like receptor 3; and WT, wild‐type.