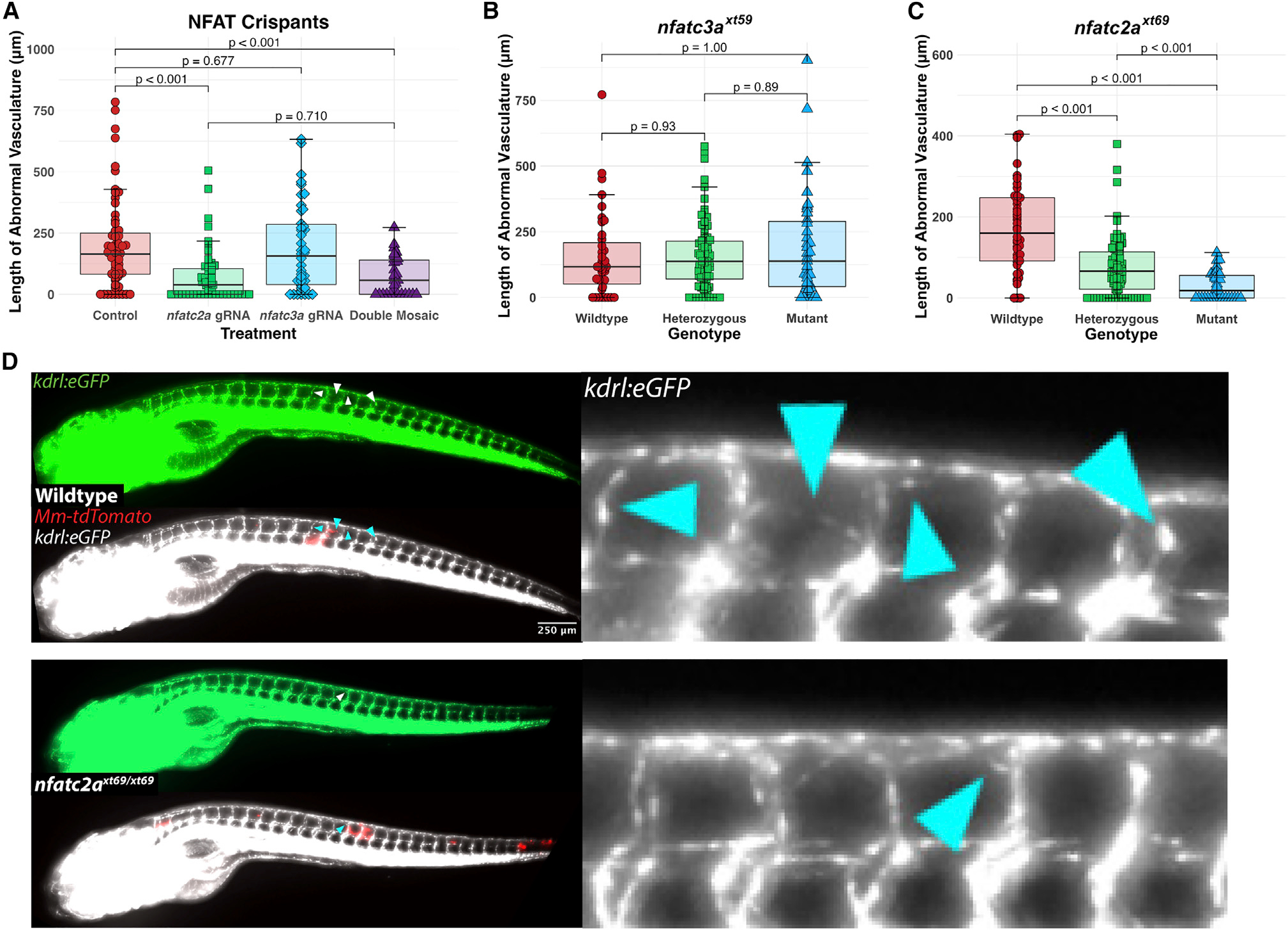
Figure 3. nfatc2a, but not nfatc3a, is required for the angiogenic response to mycobacterial infection in vivo
(A) Quantitation of ectopic vasculature from sgRNP-injected, Mm-infected kdrl:eGFP larval zebrafish. A single high-scoring sgRNA was selected from CRISPRscan and injected either singly (nfatc2a gRNA, nfatc3a gRNA) or at an identical total RNA mass (double mosaic). At 2 dpf, these were infected along the trunk with Mm-tdTomato and imaged at 4 days post infection (dpi). Each point represents a single larva. Control fish are uninjected siblings. n = 63 control, 55 nfatc2a, 42 nfatc3a, 31 double mosaic. Statistics are from Dunn?s Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparisons test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment for independent tests. Representative of three biological replicates. Additional replicates provided in Figures S2A and S2B.
(B) Blinded quantitation of angiogenic vessels from larvae from a heterozygous incross of kdrl:eGFP; nfatc3axt59/+ fish demonstrated no differences across the genotypes, confirming preliminary findings in (A). Data from a single experiment, n = 39 wild-type, 89 heterozygous, 39 homozygous mutant. Statistics by Dunn?s Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparisons test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment.
(C) Quantitation of angiogenesis from a heterozygous incross of kdrl:eGFP; nfatc2axt69/+ fish under genotypic blinding. Homozygous mutant fish display an average of ?30%?90% reduction in the length of angiogenic vessels. Representative of three independent experiments (additional replicates in Figures S2E and S2F). Statistics by Dunn?s Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparisons test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment. n = 44 wild-type, 92 heterozygous, 35 homozygous mutant.
(D) Representative images from kdrl:eGFP; nfatc2axt69/xt69 and kdrl:eGFP; nfatc2a+/+ larvae. Vascularization in the homozygous mutant is notably reduced compared with wild type. Arrowheads indicate areas of neovascularization.