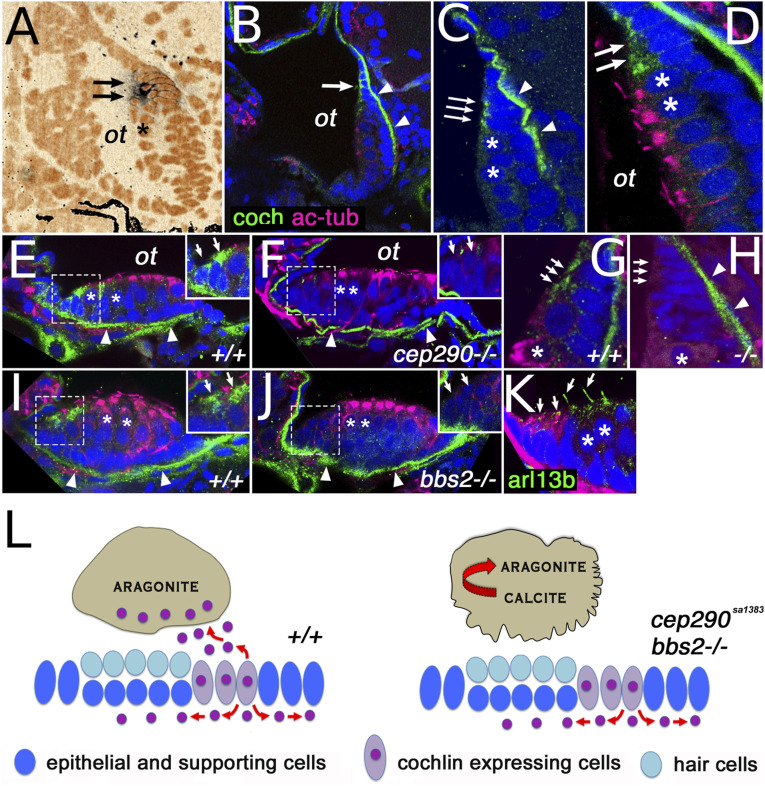
Fig. 5
Cochlin expression pattern. (A) cochlin transcript expression (arrows) in the posterior macula of the zebrafish otic vesicle at 5 dpf. (B and C) Cochlin protein expression (in green) in the posterior macula at 5 dpf. (D) Cochlin expression (in green, arrows) at the dorsal rim of the posterior macula in cells immediately adjacent to hair cells (asterisks). (E?H) Cochlin protein localization in anterior (E and F) and posterior (G and H) maculae of wild-type and cep290sa1383 homozygotes as indicated at 5 dpf. (I and J) Cochlin expression in the anterior macula of wild-type (I) and bbs2?/? mutants (J). (K) Cilia visualized with Arl13b-GFP transgene (in green, arrows), Cochlin in red. (L) Model of cep290 and bbs2 function in Cochlin secretion. Loss of cep290, bbs2, and most likely other cilia-related genes leads to defects apical Cochlin secretion into the ear lumen and causes abnormal crystallization of otolithic calcium carbonate. In (D?K), sections are double stained for acetylated tubulin (in magenta), which accumulates apically in hair cells. All sections are counterstained with DAPI in blue (pseudocolored in orange in A). Insets in (E, F, I, and J) show enlargements of Cochlin-secreting cells (enclosed in dashed line boxes). In (B?J), the arrows indicate Cochlin-secreting cells and the arrowheads point to Cochlin presence in the basal lamina. ?ot? otolith position, asterisks indicate hair cells. CaCO3 crystal structure after ref. 36.