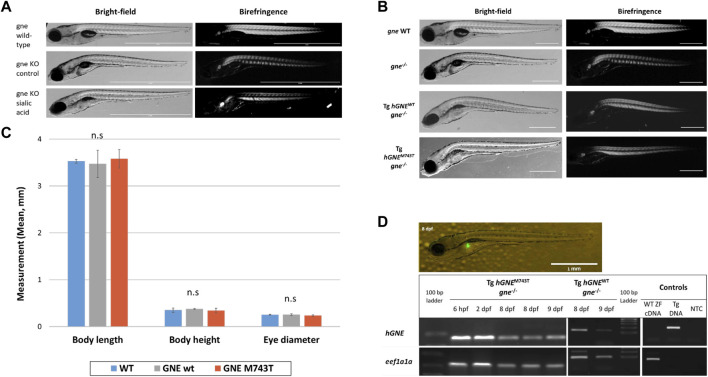
FIGURE 8 Exogenous sialic acid or hGNE transgene expression does not rescue the gne KO larvae. (A) Brightfield and birefringence representative images of 8 dpf larvae that participated in the sialic acid supplementation experiment: gne WT (top), gne KO (middle) and gne KO larvae with 800 ?M sialic acid supplementation (bottom). The addition of sialic acid did not ameliorate the muscle phenotype, nor rescued gne KO larvae from mortality at 8?10 dpf. (B) Brightfield and birefringence images of GNE myopathy genetic model larvae display a phenotype similar to gne KO larvae at 8 dpf. (C) No significant differences were detected in morphologic measurements (body length, body height, eye diameter) between wild-type and hGNEM743T or hGNEWT transgenic KO models at 8 dpf. (Mann-Whitney Wilcoxon test, p > 0.05). Means of 10 larvae/variable/genotype and corresponding standard deviations are presented. (D) Transgene expression validation. Top: Fluorescent image of a representative 8 dpf Tg(ins:EGFP;hGNEM743T;gne?/?) larva showing EGFP expression in the pancreas. Scale bar = 1 mm. Bottom: Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR amplification products of the hGNE cDNA and eef1a1a. cDNA samples from both hGNEM743T and hGNEWT transgenic KO models show the expected amplification in all tested time points. Non-transgenic WT zebrafish cDNA (WT ZF cDNA) and genomic DNA from transgenic fish (Tg DNA) served as controls for each target. (NTC) no template control.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol