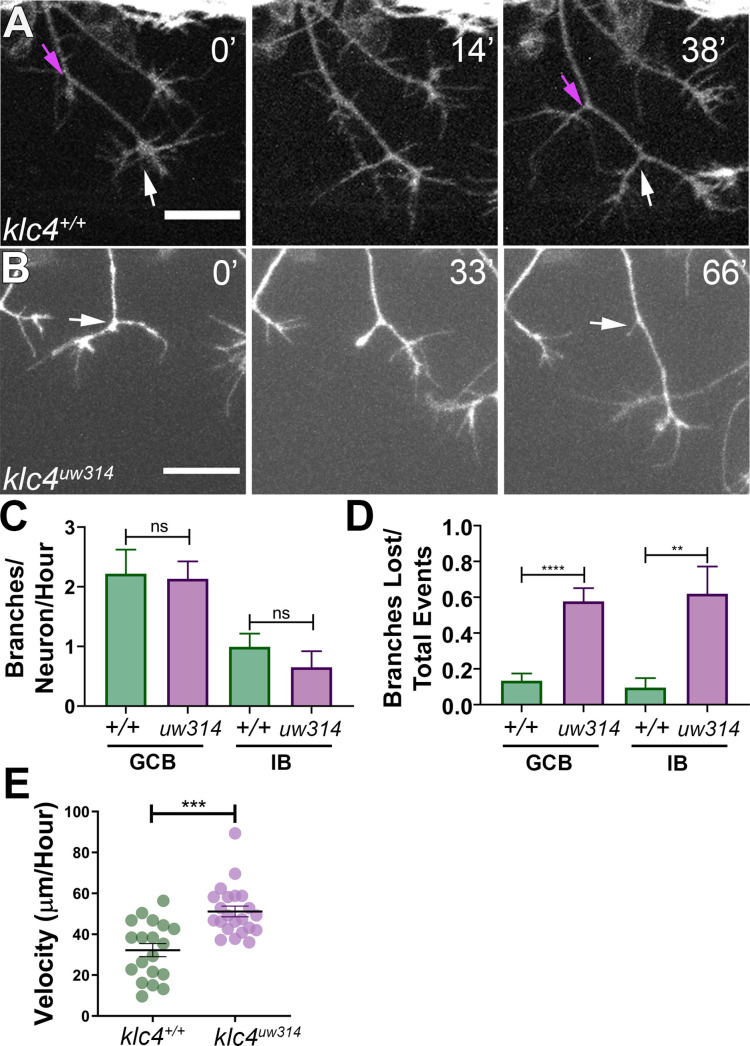
Figure 3
(A) A wild type axon forms stable branches by growth cone bifurcation (GCB, white arrows) and interstitial branching (IB, magenta arrows) over the course of 38? min. (B) A klc4uw314 mutant axon initiates a branch via GCB (0minutes, white arrow), but one branch begins to retract and is nearly fully gone after 66? min (panel 3, white arrow). 20 Ám scale bar. (C) Quantification of axon branch initiations per neuron per hour in wild type and mutant embryos wild type GCB mean = 2.22 branches/neuron/hr, N=11 neurons from 4 embryos. Klc4uw314 GCB = 2.13 branches/neuron/hr, N=14 neurons from 4 embryos. Wild type IB=0.99 branches/neuron/hr, N=10 neurons from 4 embryos. Klc4uw314 IB = 0.65 branches/neuron/hr, N=8 neurons from 4 embryos. Error bars = SEM. There was no significant difference in branch initiation between wild type and mutant axons. GCB P=0.73, IB P=0.15, Mann?Whitney test. (D) Quantification of branches that retracted after initiation in wild type and klc4uw314 embryos. Data are displayed as a branch loss ratio (branches retracted/total branching events). Branches created by either GCB or IB were both more likely to retract in klc4uw314 embryos (wild type GCB mean = 0.13, N=11 neurons from 4 embryos; klc4uw314 GCB = 0.58, N=14 neurons from 4 embryos; wild type IB = 0.10, N=10 neurons from 4 embryos; klc4uw314 IB = 0.62, N=8 neurons from 4 embryos). **p=0.0055, ****p<0.0001, Mann?Whitney test. Error bars = SEM. (E) Quantification of axon growth velocity. Axons in klc4uw314 mutants grow faster than in wild type. Wild type N=19 axons from 3 embryos. Klc4uw314 N=22 axons from 4 embryos. ***P=0.0001, Mann-Whitney test. Error bars = SEM.
Branches initiate but do not stabilize in klc4uw314 mutants.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife