Fig. 9
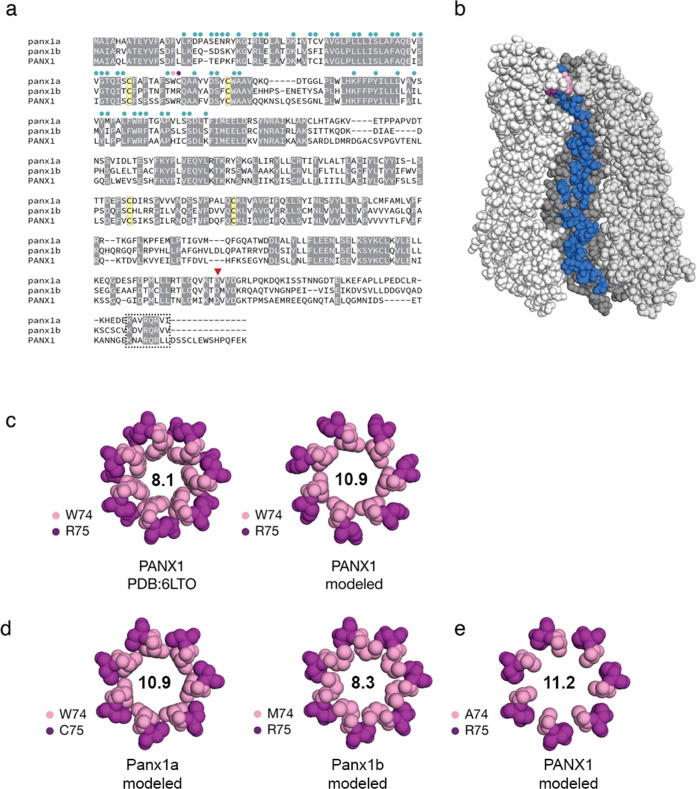
a Protein sequence alignment of full-length human pannexin-1 (PANX1; amino acids (aa): 1-426) and zebrafish Panx1a (aa 1-416), and Panx1b (aa 1-422). Circles above the sequence alignment indicate amino acids that line the channel. Two amino acids at positions 74 and 75 form an extracellular gate (in pink and purple, respectively). Four cysteines (in yellow) contribute to two functionally important disulfide bonds. A red triangle denotes a caspase cleavage site located in the carboxyterminal domain. A box indicates a conserved carboxy-terminal segment of unknown significance. b Amino acids that line the inside of the channel are shown on one monomer of heptameric human PANX1 (PDB: 6LTO; aa 1-341 55). The channel is oriented with the extracellular-facing side of the channel at the top. c The human PANX structure was used to model the extracellular gate of zebrafish Panx1a/Panx1b by substituting as required and repacking only amino acids 74/75 against a rigid backbone. As a control, human PANX1 was subjected to the same refinement and repacking protocol, creating a larger extracellular gate than the original cryo-EM structure. The diameters of the respective gates (in angstroms) are shown. d Molecular models of the extracellular gates of zebrafish Panx1a/Panx1b. Each protein bears one substitution relative to the human PANX1 structure. e An alanine was modeled to mimic a constitutively ATP-permeable state. Molecular graphics were produced with PyMOL v2.4.1 (Schrödinger, LLC).